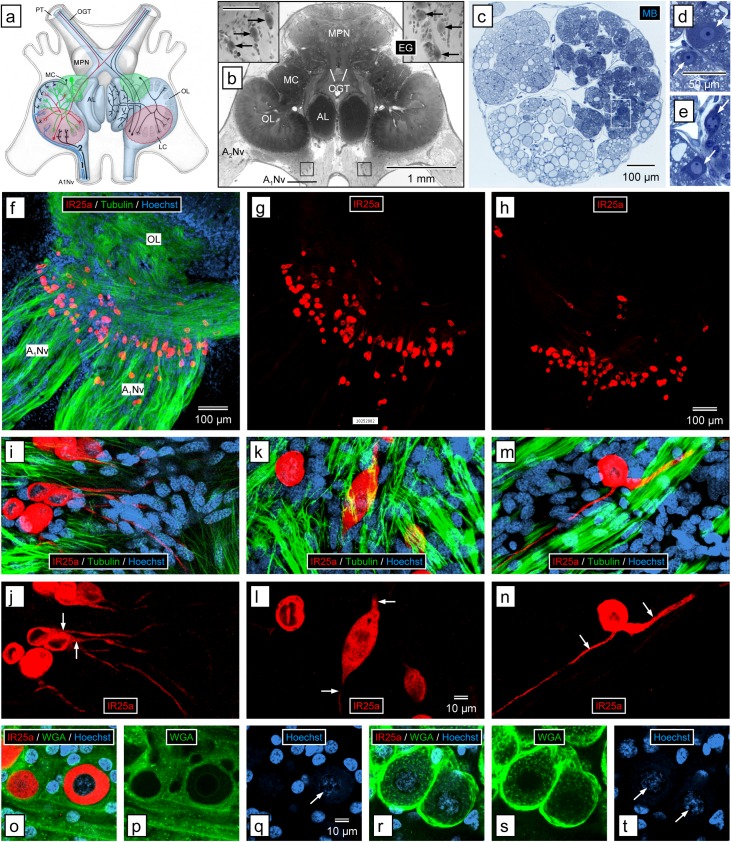
Fig 7. Immunolabeling with anti-HaIR25a in the brain.
(a) Schematic drawing of the olfactory pathway (light blue overlay) in the brain of P. argus (modified from Schmidt and Ache (1996) [8]). Afferent axons of ORNs (1, blue) enter the brain via the antennular nerve (A1Nv) and project to the ipsilateral olfactory lobe (OL) where they terminate in one of its cone-shaped glomeruli. The OL is closely linked to another glomerular neuropil, the accessory lobe (AL). OL and AL are innervated by local interneurons (green) whose somata form the medial soma clusters (MC) and ascending projection neurons (red) whose somata form the lateral soma clusters (LC). Axons of projections neurons form the olfactory glomerular tracts (OGT) that run within the protocerebral tracts (PT) connecting the brain with the eyestalk ganglia. Median protocerebral neuropils (MPN). (b) Horizontal section through brain stained with ethyl gallate (EG). Large cells (arrows in insets) are located in the axon sorting zone of the A1Nv before it reaches the OL. Location of insets is shown by black squares; scale bar in left inset is 100 μm and also applies to right inset. Antenna 2 nerve (A2Nv). (c–e) Cross section through the antennular nerve where it enters the brain, stained with methylene blue (MB). (c) Low magnification. The axon fascicles in the antennular nerve form three large divisions. The lateral division is formed by axon fascicles from the lateral flagellum that are more intensely stained than other axon fascicles (because they contain numerous extremely thin ORN axons). Large, intensely stained cells selectively occur in the lateral division (white rectangle). (d, e) Large, intensely stained cells (arrows) in the lateral division of the antennular nerve at higher magnification. (e) Region highlighted in (c). The large cells have voluminous cytosol and a spherical nucleus containing at least one dense nucleolus. (f, g) Confocal image of a sagittal section through brain labeled with anti-HaIR25a (red), anti-tubulin (green), and Hoechst 33258 (blue) at low magnification); scale bar in (f) also applies to (g). (f) Overlay of all three fluorescence channels. (g) anti-HaIR25a channel. Anti-HaIR25a intensely labels a loose assembly of about 100 large cells located in the axon sorting zone of the A1Nv before it reaches the OL. Axons within the antennular nerve are intensely labeled by anti-tubulin but not by anti-HaIR25a, and HaIR25a-positive cells are not labeled by anti-tubulin. (h) Confocal image of a sagittal section through brain of different animal labeled with anti-HaIR25a at low magnification () shows a similar assembly of about 100 intensely labeled large cells in the axon sorting zone of the antennular nerve. (i–n) Morphology of single large cells in the axon sorting zone of the antennular nerve labeled with anti-HaIR25a (red), anti-tubulin (green), and Hoechst 33258 (blue) at high magnification (confocal images). Scale bar in (l) applies to all images. (i, k, m) Overlay of all three fluorescence channels. (j, l, n) anti-HaIR25a channel. (i, j) Unipolar cells. Most of the HaIR25a-positive cells have one process (arrows) projecting from the cell body. Generally, this process projects toward the OL. (k, l) Bipolar cell. Some of the HaIR25a-positive cells have two processes (arrows) projecting from both poles of the cell body. (m, n) Pseudo-unipolar cell. Rarely HaIR25a-positive cells have two processes (arrows) projecting from the same region of the cell body. (o–t) Double-labeling with anti-HaIR25a (red) and WGA-AF488 (Hoechst 33258—blue) at high magnification (confocal images). Scale bar in (q) applies to all images. (o, r) Overlay of all three fluorescence channels. (p, s) WGA-AF488 channel. (q, t) Hoechst 33258 channel. (o–q) Large cells in the axon sorting zone of the OL. (r–t) Neuronal somata in the medial soma cluster. Large cells in axon sorting zone are intensely labeled by anti-HaIR25a but not by WGA whereas somata in the MC are not labeled by anti-HaIR25a but are intensely labeled by WGA. Nuclei of large cells and neurons (arrows) are similar in shape (spherical) and in having very loose heterochromatin (Hoechst labeling of low intensity).