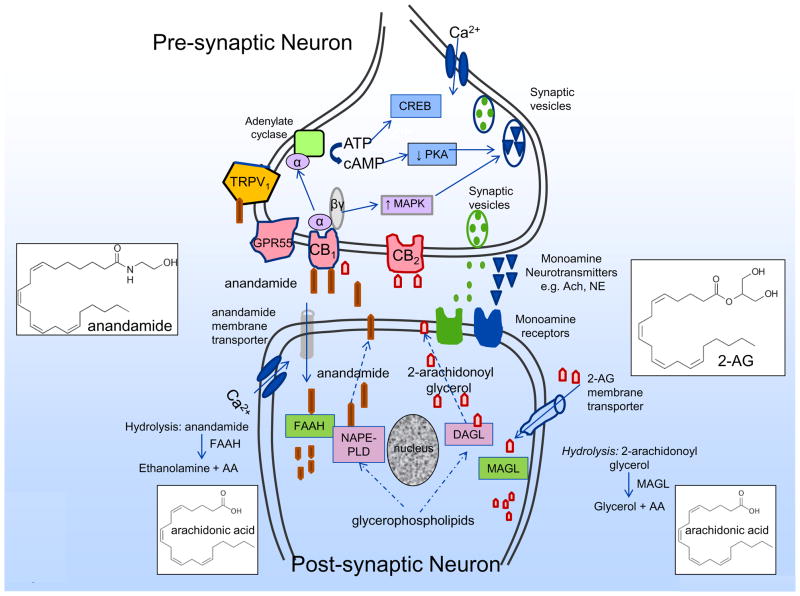
Figure 2.
Synthesis, action and hydrolysis of endocannabinoids. Endocannabinoids (e.g. anandamide, 2-arachidonoylglycerol) are synthesized in postsynaptic neurons by synthetic enzymes such as NAPE-phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) and diacyl glycerol lipase-α (DAGLα) respoectively. Endocannabinoids released into the synaptic cleft function as retrograde messengers binding to the presynaptic receptors including CB1, CB2, GPR55 and TRPV1, and through various effectors, reduce activity of protein kinases (e.g. PKA), increase activity of MAP kinases, and thereby modulate channels and monoamine neurotransmitter release e.g. acetyl choline, norepinephrine. Endocannabinoids undergo re-uptake into the post-synaptic neuron by membrane transporters and hydrolysed by enzymes such as fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacyl glycerol lipase (MAGL).