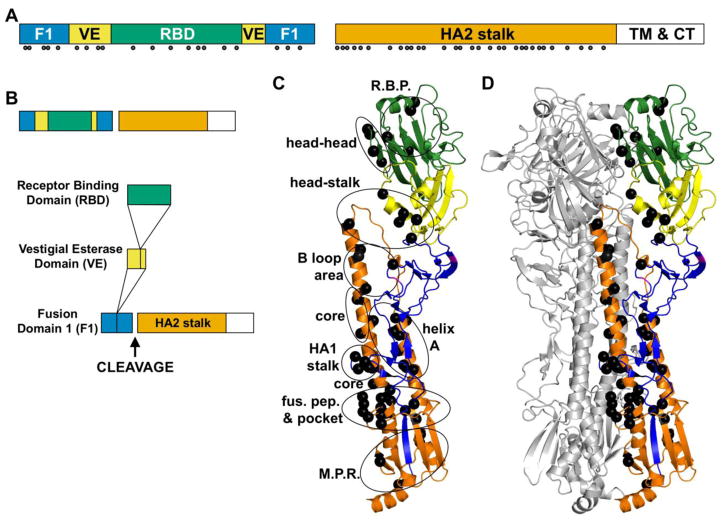
Figure 3. Prefusion structure of the HA protein and residues known to affect its stability.
(A) HA domain structure. HA1 domains include the fusion (F1, blue), vestigial esterase (VE, yellow), and receptor-binding domain (RBD, green). HA2 includes a stalk domain (orange), transmembrane region (TM, white), and cytoplasmic tail (CT, white). Solid circles identify residues to which stabilizing or destabilizing mutations have been identified in review articles [21, 22] and primary manuscripts [54, 60–62, 66, 70, 74–87]. (B) Domain insertion in the HA protein, adapted from [116]. (C) Prefusion structure of one HA monomer. (D) Prefusion structure of an HA trimer. Residues regulating stability (black balls) are located throughout the trimer in the receptor-binding pocket (R.B.P.), between HA1 heads (head-head), between the HA1 head the stalk (head-stalk), in the B loop and adjacent helix C (B loop area), in the core of the coiled coil (core), in the HA1 stalk, between helix A and the coiled coil (helix A), in and around the fusion peptide pocket (fus. pep. & pocket), and in the membrane-proximal region (M.P.R.). In panel D, two protomers are colored gray. Structures were generated using MacPYMOL using A/California/4/2009 (H1N1) protein data bank structure 3UBE [117].