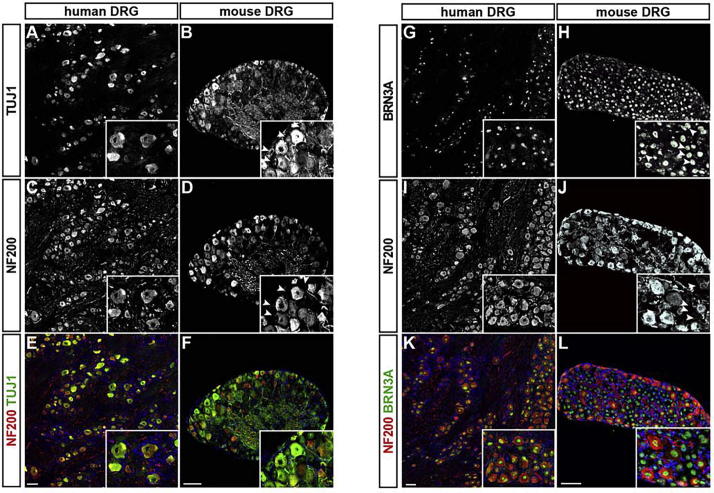
Fig. 7.
Most if not all human DRG neurons express the neurofilament heavy (NEFH; NF200) polypeptide. (A–L) Immunohistochemistry using antibodies to detect β-tubulin III (Tuj1), a pan-neuronal marker, BRN3A, a pan-sensory marker and neurofilament heavy (NF200) to label human and mouse DRG tissue sections. Two different NF200 antibodies have been used: (C–F) chicken anti-NF200 from Millipore and (I–L) mouse anti-NF200 (clone N52) from Sigma. Double fluorescence antibody labeling for Tuj1 (A, B, E and F) and NF200 (C–F) in human (A, C, E) and mouse (B, D, F) DRG sections and for BRN3A (G, H, K and L) and NF200 (I–L) in human (G, I, K) and mouse (H, J, L) DRG sections (Tuj1: green; NF200: red; E, F: BRN3A: green; NF200: red; K, L). Representative monochromatic images are shown in A–D and G–J and overlays are presented in E–F and K–L. Inserts show close-ups with arrowheads depicting mouse neurons being positive for Tuj1 (B) or BRN3A (H) but negative for NF200 (D) and (J). Note that in human DRGs almost no NF200 negative neurons were found. Scale bar = 100 μm. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)