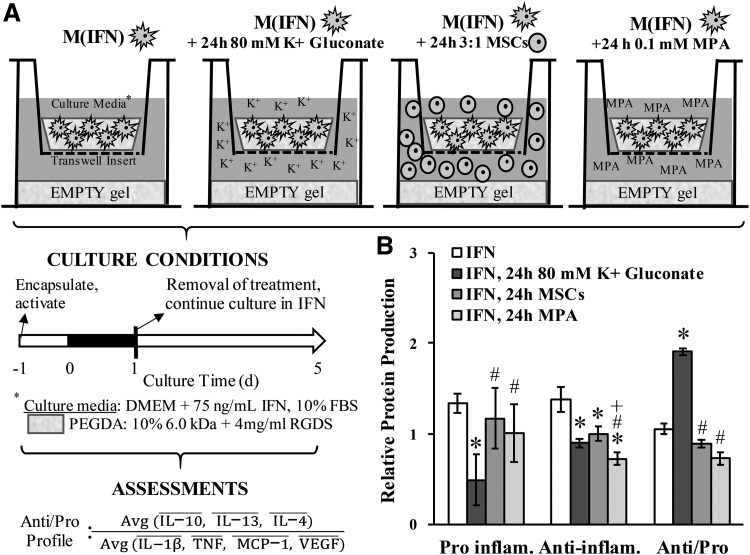
FIG. 1.
(A) Experimental design mimicking an IA injection in vitro. M(IFN)s were cultured for 5 days in the continued presence of IFN, with 80 mM K+ applied only during the first day and then removed. Other IA injection formulations—human MSCs and MPA—were also included to gain a sense of efficacy and benchmark against current OA treatments. An empty PEGDA hydrogel (∼50 kPa stiffness) was provided at the bottom of the culture well to create a surface that more closely matches the stiffness of articular cartilage (aggregate modulus ∼500 kPa12) than traditional plastic 2D surfaces (∼1 × 106 kPa). MSC behavior is known to respond to substrate stiffness. Assessments for treatment efficacy included cell lysate levels of several proinflammatory markers, anti-inflammatory markers, and the ratio between anti/proinflammatory profiles. A bar above the protein denotes normalization. (B) Relative protein production of pooled proinflammatory and pooled anti-inflammatory molecules and the ratio between anti/proinflammatory profiles in Raw 264.7 MΦs after 5 days in culture. Treatments were applied only during the first day of culture. *Denotes a significant difference relative to IFN controls. #Denotes a significant difference relative to 24-h 80 mM K+ gluconate. +Denotes a significant difference relative to 24-h MSCs. PEGDA, poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; MPA, methylprednisolone acetate.