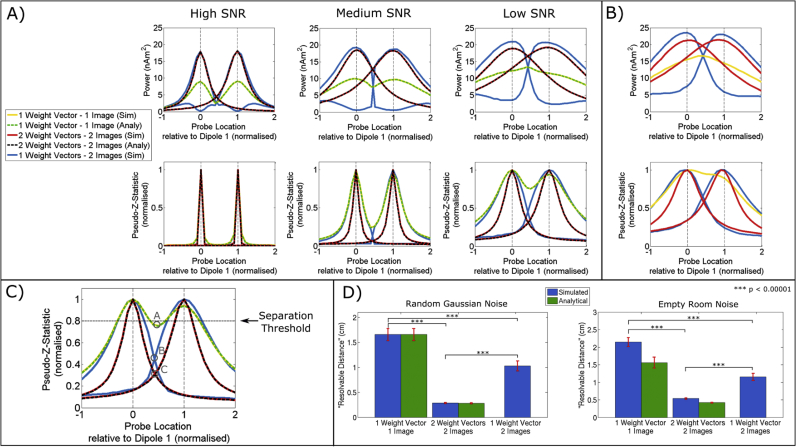
Fig. 2.
Simulation results. A) Beamformer projected power (top) and pseudo-z-image (bottom), for the three beamformer implementations (Single weight vector; single image (yellow). Single weight vector; two images (blue). Two weight vectors; Two images (red) – dashed lines show analytical images computed in the infinite integration limit). The case of high, medium and low SNR are shown in the left, centre, and right plots respectively. Sensor noise is Gaussian. B) Equivalent to (A) but the interference is taken from an empty room. C) Schematic diagram showing how spatial separation of two sources was calculated: the amplitude of the local minima between the peaks (points marked A, B and C) had to be less than 80% of the maximum peak height. D) Spatial resolution for the 3 different beamformer implementations. The left hand plot shows the case for Gaussian noise and the right hand plot shows the case for empty room noise.