Fig. 3.
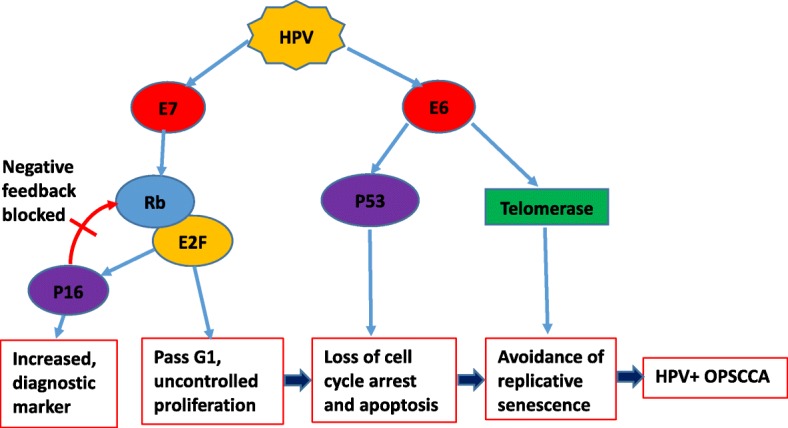
E6 and E7 are the main oncoproteins. They are encoded by HPV and disrupt or usurp multiple cellular signaling pathways to maintain infected cells in a proliferative state that facilitates viral persistence and replication. HPV E7 oncoprotein inactivates the Rb protein family, resulting in over-activation of E2F transcription factor with increased transition of cell from G1 to S phase and cell proliferation. Inactivation of Rb proteins also results in increased levels of p16, a marker for HPV infection diagnosis. E6 degrades p53 protein, deregulating cycle checkpoints, and activates telomerase through the transcriptional upregulation of an important subunit of human telomerase, maintaining the telomere length. E7 and E6 have complementary effects
