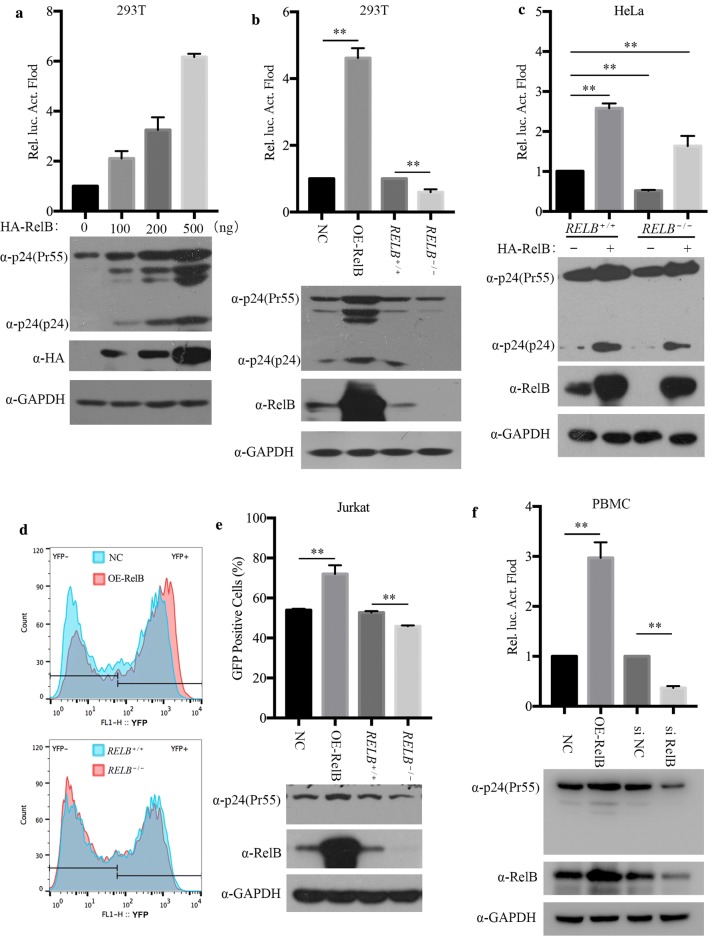
Fig. 8.
RelB increases HIV-1 gene transcription. a HEK 293T cells (0.5 × 106) in a 6-well plate were transfected with increasing amounts of pHA-RelB, together with pVSV-G (0.3 μg) and pNL4-3.Luc.env−. (1 μg). Forty-eight hours post transfection, cells were collected for western blotting and luciferase activity analysis. b Stable RelB-overexpressing cells, RELB−/− cells, and control HEK 293T cell lines (0.5 × 106) were transfected with pVSV-G (0.3 μg) and pNL4-3.Luc.env− (1 μg). Western blotting and Luciferase activity essays were performed to assess viral gene expression. c Control and RELB−/− HeLa cells were transfected with pHA-RelB (500 ng) or vector DNA. Twenty-four hours post transfection, cells were infected with VSVG-NL4-3.Luc.env− equivalent to 20 ng p24 for 40 h. Cells were collected for luciferase assay and western blotting analyses. d and e RelB overexpressing or RELB−/− Jurkat cells were infected with VSVG-NLENY1-ES-IRES equivalent to 20 ng p24 for 48 h. Gating on live Jurkat cells was based on size (FSC-H) and granularity (SSC-H). YFP positive cells were scored by flow cytometry 48 h after infection (d). Results from three independent experiments were summarized, and cells were collected for western blotting analysis (e). f PBMCs (2 × 106) were infected with RelB-expressing VLPs, or transfected with siRNA. After 24 h, infection with VSV-G pseudotyped NL4-3.Luc.env− (equivalent to 500 ng p24) was performed by spinoculation at 300×g for 30 min. After 24 h, whole cell lysates were examined in luciferase assay and western blotting with the indicated antibodies