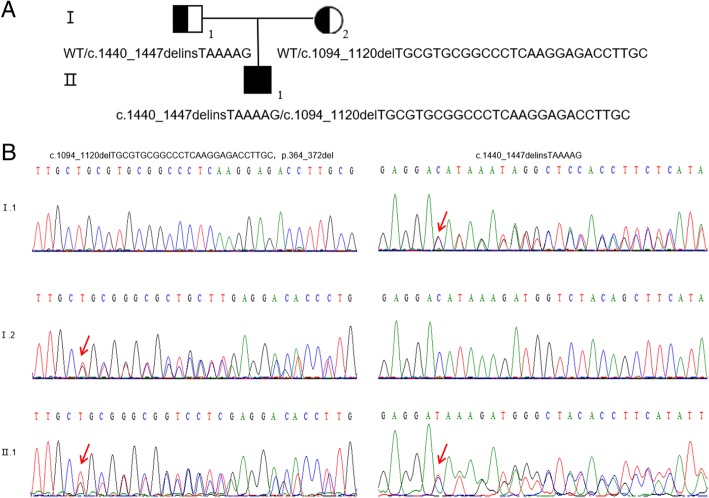
Fig. 3.
Mutation analysis by direct DNA sequencing. a Pedigree illustrating the segregation of the mutant alleles to the index patient (II.1). b The left panel shows the deletion at c.1094_1120delTGCGTGCGGCCCTCAAGGAGACCTTGC, which results in the deletion of nine amino acids at position 364_372 (p.364_372del). The mother (I.2) and the patient (II.1) are heterozygous for c.1094_1120delTGCGTGCGGCCCTCAAGGAGACCTTGC mutation, whereas the father shows the wild-type sequence at this position. The indel mutation c.1440_1447delinsTAAAAG, leading to original stopcodon lost, results in elongated protein. The patient was found to be heterozygous for this mutation was found in the heterozygous state in the patient (II.1) and the father (I.1). The mother carries the homozygous wild-type allele at this position