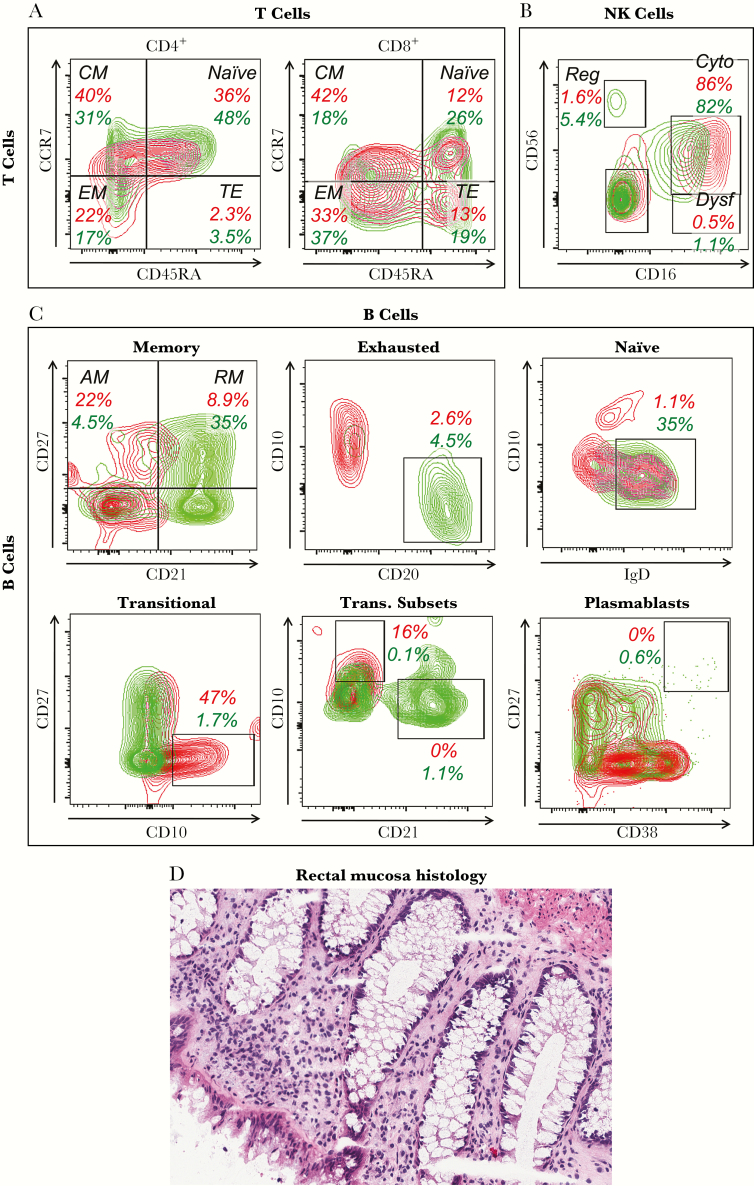
Figure 2.
Immune cell phenotyping. (A–C) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained on day 3324 after exposure were analyzed by flow cytometry of singlet viable lymphocytes (by forward and side scatter and dye exclusion). The red plots and numbers represent the subject of this study, and the green plots and numbers represent a typical human immunodeficiency virus-1-uninfected control. (A) Differentiation status of blood CD4+ and CD8+ T cells as defined by CD45RA and CCR7 after gating on CD3+ cells. Percentages across all CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are given. (B) Natural killer (NK) cell subsets defined by CD16 and CD56 after gating on CD3−/CD19−/HLA DR−/CD11c− cells. Percentages across all NK cells are given. (C) B-cell subsets are delineated as subpopulations of total B cells defined as CD3−/CD16−/CD19+. Percentages across all B cells are given. Memory B cells are defined using CD21 and CD27. Exhausted B cells are defined by subgating on the CD27−/CD21− B cells from (D), as CD20+/CD10− cells. Naive B cells are defined by subgating on the CD27−/CD21+ B cells from (D), as IgD+/CD10− cells. Transitional-immature B cells are defined as CD10+/CD27−. The transitional B cells in (G) are further subclassified as less immature expressing CD21high/CD10low versus more immature expressing CD21low/CD10high. Plasmablasts are defined as CD27high/CD38high. (D) Rectal mucosal histology (hematoxylin and eosin staining) is shown. Abbreviations: AM, activated memory (CD27+/CD21−); CM, central memory; Cyto, cytotoxic; Dysf, dysfunctional; EM, effector memory; Reg, regulatory; RM, resting memory (CD27+/CD21+); TE, terminal effector.