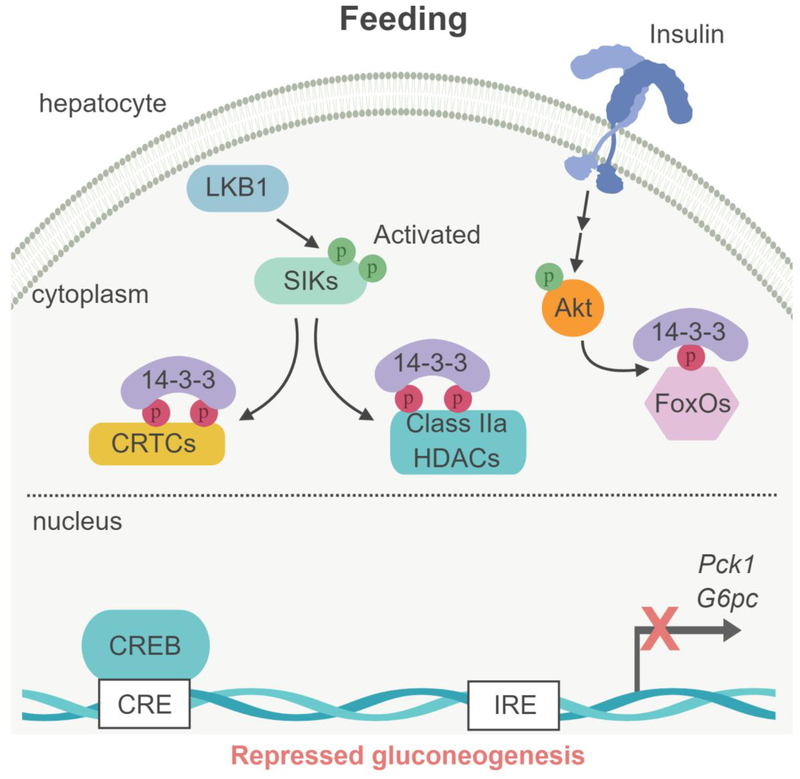
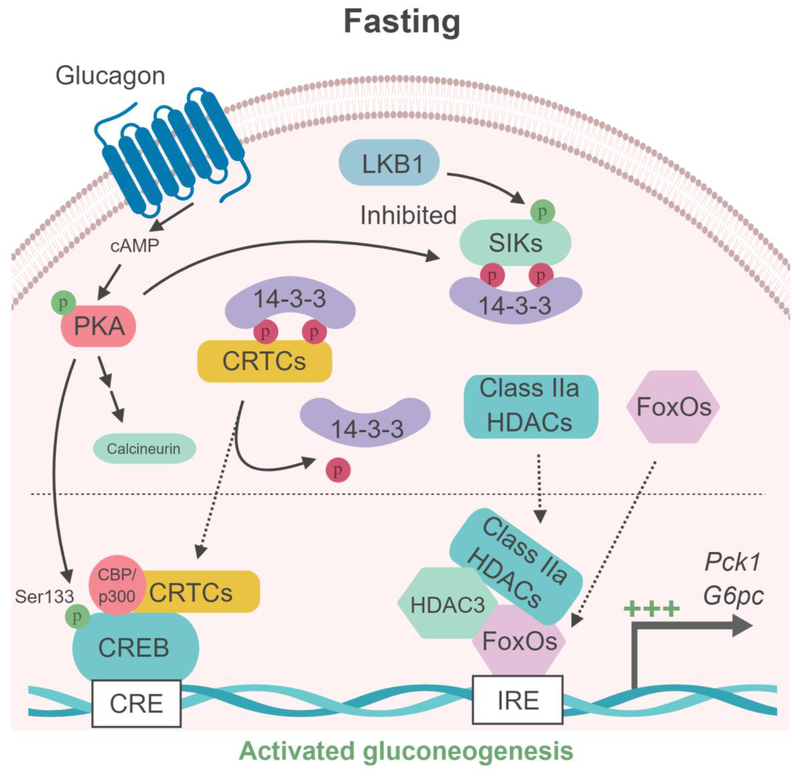
Figure 3. Model of SIK-dependent gluconeogenesis regulation in liver.
(Left box) Under feeding conditions, Akt-dependent phosphorylation of the FoxOs transcription factor results in binding to 14–3–3 proteins, sequestering FoxOs into the cytoplasm. In parallel, the LKB1-dependent SIKs activation induces the phosphorylation of the cofactors CRTCs and class IIa HDAC and their binding to the 14–3–3 proteins and retention into the cytoplasm, leading to the repression of gluconeogenic gene expression (G6pc and Pck1). (Right box) During fasting, glucagon/cAMP-activated PKA phosphorylates the transcription factor CREB on Ser133, promoting the recruitment of the coactivator proteins CBP/p300. In parallel, PKA inhibits SIKs through phosphorylation-dependent interactions with 14–3–3 proteins, resulting in loss of CRTCs and HDACs phosphorylation. Glucagon-PKA pathway also activates the phosphatase calcineurin, which contributes to CRTCs dephosphorylation. Dephosphoryled CRTCs and class IIa HDACs then translocate to the nucleus where CRTCs cooperate with CREB and CBP/p300 while class IIa HDACs recruit HDAC3 causing deacetylation of FoxOs to gluconeogenic gene promoters to activate their transcription. CRE : cAMP responsive element; IRE : insulin responsive element.