Figure 2. Examples of population level engineering via cell-to-cell communication.
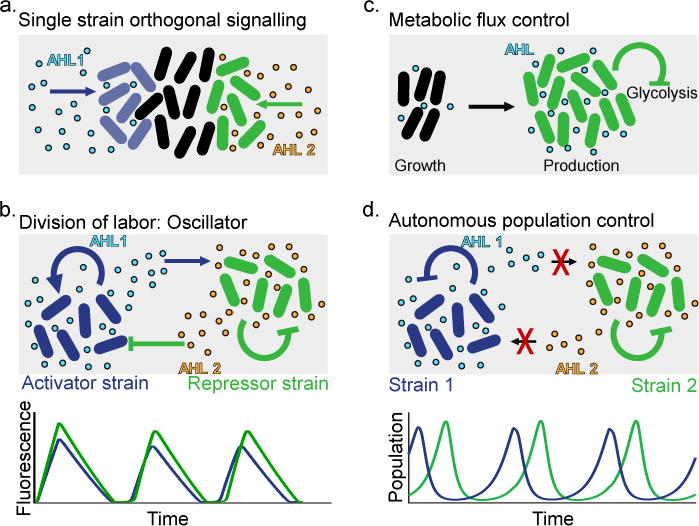
(a) Orthogonal spatial response to two different quorum sensing (QS) signals in a double-receiver strain, achieved by optimizing promoter sequence and receiver protein levels [67] (sender cells for AHL 1 and AHL 2 not shown). (b) Division of labor between two strains, each implementing part of a classical oscillator circuit [63]. The activator strain contains a positive feedback loop involving AHL 1, whereas degradation of QS molecules is triggered in both strains by AHL 2, which is produced by the repressor strain in response to AHL 1. These positive and negative feedback loops spanning both strains lead to emergent oscillations. (c) QS circuit suppressing glycolysis at a critical cell density [79]. Trade-off optimization between biomass production, overflow metabolism and flux through a heterologous pathway maximizes product yield. (d) Population control with tunable dynamics via QS-triggered lysis [64,81]. Self-limitation of individual strains stabilizes co-cultures (oscillatory regime shown), with no communication between strains required.
