Figure 1. Misfolding-associated protein secretion (MAPS).
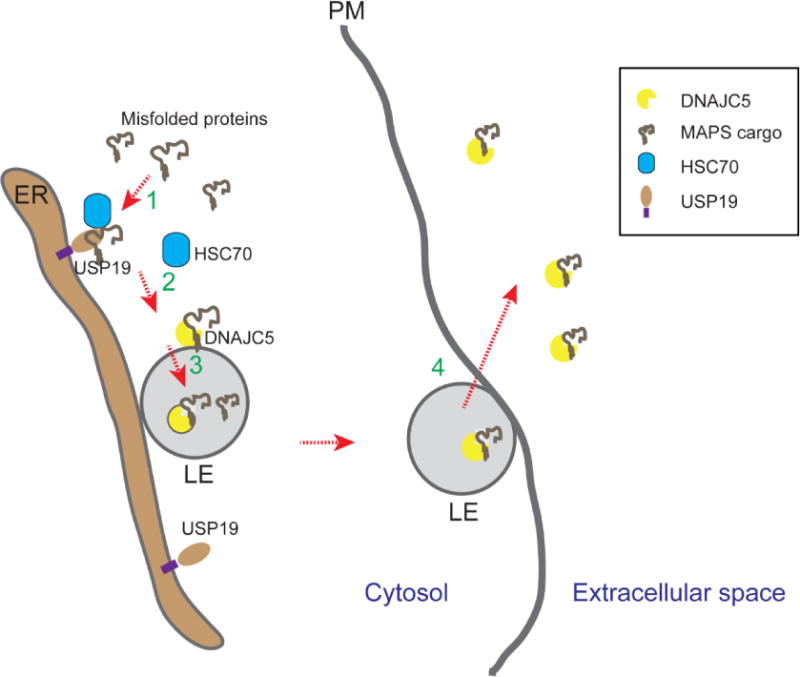
Misfolded cytosolic proteins can be secreted by MAPS following these steps. In step 1, misfolded proteins are enriched on the surface of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by binding to a receptor (e.g. USP19) that has a chaperone activity. For USP19-mediated secretion, USP19-associated chaperone HSC70 may assist USP19 in substrate recruiting. In step 2, misfolded proteins are transferred to DNAJC5, a HSC70 co-chaperone that is associated with the membrane of late endosomes (LE) (Note that Les are generally in close contact with the ER). Next, the complex of DNAJC5 and misfolded proteins are moved into the lumen of late endosome via a mechanism that is unclear. In step 4, late endosomes contact and fuse with the plasma membranes (PM) to release misfolded proteins.
