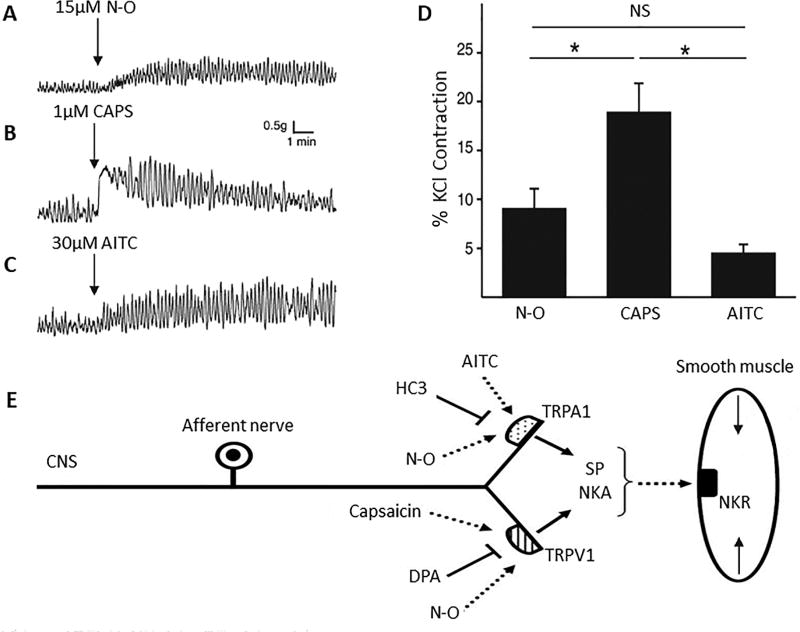
Figure 4.
Examples of agonist-induced phasic contractions in rat bladder strips showing that NO2-OA (N-O) mimics the effects induced by activation of TRPV1 or TRPA1 receptors. D. Arrows indicate time of application of NO2-OA (15µM, A), CAPS (1µM, B) and AITC (30µM, C). (D) Summary data showing the amplitude of agonist-induced increases in phasic contraction amplitude normalized to KCl-evoked contraction). * p < 0.05, NS p > 0.05 by one-way ANOVA, n = 9 to 13. E, Schematic of NO2-OA mechanism of action. NO2-OA activates TRPV1 and TRPA1 channels on capsaicin-sensitive afferent nerve terminals to trigger the release of neurokinins that act on postjunctional receptors to induce smooth muscle contractions. SP – substance P, NKA – neurokinin A. NKR – neurokinin receptor. Reproduced with permission from Artim et al., 2011 [18].