Figure 2.
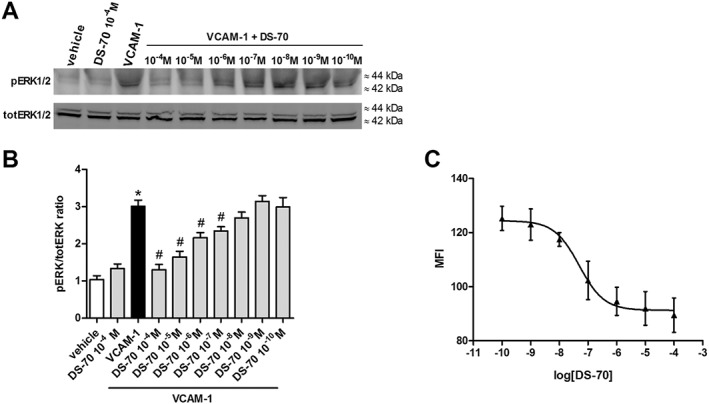
DS‐70 reduces, in a concentration‐related manner, VCAM‐1‐induced ERK 1/2 phosphorylation (pERK 1/2) in Jurkat E6.1 cells and VCAM‐1 binding to Jurkat E6.1 cells exposed to PE‐conjugated HUTS‐21 mAb. (A) Jurkat E6.1 cell extracts were assayed for pERK 1/2 by Western blotting; a representative assay is shown. Control cells plated on VCAM‐1 had a much stronger signal for pERK 1/2 than vehicle‐treated cells. DS‐70 reduces VCAM‐1‐induced pERK1/2, whereas, at a higher concentration (10−4 M), it was not able to modify pERK1/2 in the absence of this adhesion molecule. (B) The results of semiquantitative densitometry analysis of the bands from five independent experiments are shown (mean ± SD); the amount of pERK 1/2 is normalized to that of total ERK 1/2. *P < 0.05, significantly different from vehicle; # P < 0.05, significantly different from VCAM‐1. (C) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) due to the anti‐β1 integrin mAb PE conjugated HUTS‐21 plotted against different concentrations of DS‐70 added to Jurkat E6.1 cells in the presence of VCAM‐1 (5 μg·mL−1) was measured. Each point represents the mean ± SD of five independent experiments carried out in triplicate. VCAM‐1 administered alone was able to promote epitope exposure and a significant increase of MFI over vehicle‐treated cells exposed to PE conjugated HUTS‐21 alone (MFI values were 130 ± 3 vs. 80 ± 4; n = 5. P < 0.05, significantly different from VCAM‐1 alone. Non‐specific binding of an isotype control PE conjugated mAb added to Jurkat E6.1 cells produced an MFI of 38 ± 4 (n = 5) that was subtracted from all samples.
