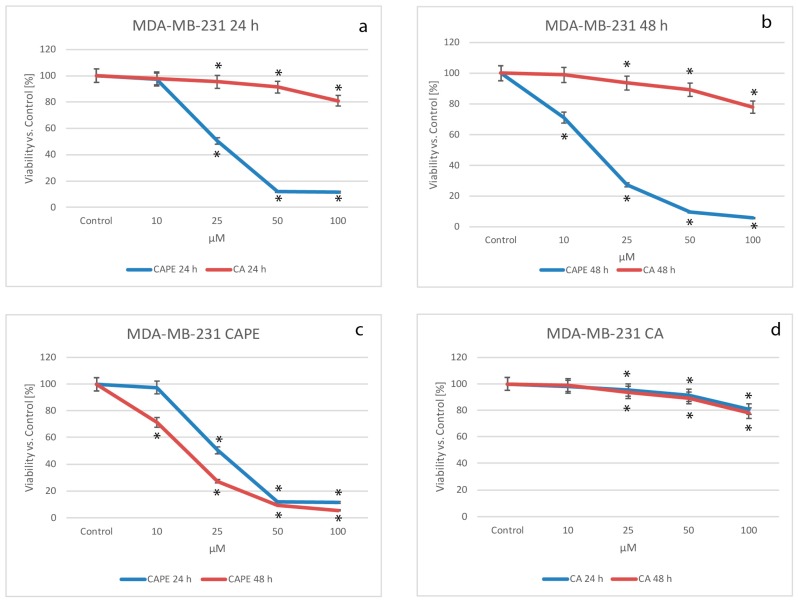
Figure 1.
Cytotoxic effects of CAPE and CA were both tested using concentrations of from 10 to 100 µM with 24 and 48 h incubation times, on the breast cancer cell line MDA-MB- 231. Both substances caused visible dose-dependent effects. Stronger activity was observed for CAPE than CA starting with a dose of 25 µM of each compound (a) following a 24 h incubation time. For the 48 h experiments (b), all doses of CAPE resulted in a much stronger cytotoxic effect than CA using corresponding doses; (c) using a dose of 10 µM of CAPE, the 48 h experiment produced a more visible cytotoxic effect when compared to 24 h, and a conspicuously stronger effect for 25 µM. However, the succeeding dose increases of CAPE (50 and 100 µM) didn’t show a significant difference in viability factor, with both reaching a very low level of viability. CA cytotoxic activity showed no significant difference over time and generally, displayed low cytotoxic activity for the MDA-MB-231 cell line (d). Cell viability was analyzed by MTT assay. The results were presented as mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments, with 12 wells each (* p < 0.05; Friedman ANOVA test).