Table 1.
In vitro cardiovascular effects of the chemical constituents of essential oils.
| Compound | Assay | Concentration | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
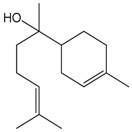 Bisabolol |
Rat smooth muscle from vascular and non-vascular | 1–1000 μmol/L | Relaxation by acting in Ca2+ voltagem-dependent channel | [49] |
| Porcine splenic artery and coronary artery | 3, 10 and 30 μM | Vasodilatation by inhibiting calcium influx | [51] | |
| Rat thoracic aorta and mesenteric ring | 1–1000 μmol/L | Vasorelaxation by acting in Ca2+ voltagem-dependent channel | [50] | |
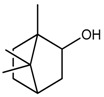 Borneol |
Human internal mammary artery | Phytotherapic preparation enriched with borneol (1 mg/mL) | Vasorelaxation with and without endothelium | [56] |
| Rat thoracic aorta artery | 10−9 to 3 × 10−4 M | Vasorelaxant effect, probably by potassium channels activation, reduction in calcium influx and inhibition of calcium mobilization from intracellular stores | [55] | |
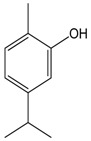 Carvacrol |
Rat thoracic aorta artery | 1, 10 and 100 μmol L−1 | Vasorelaxant effect via inhibition of ROS and stimulation of NOS | [52] |
| Rat Cerebral and cerebellar pial Arteries | 10 and 30 μM | Vasodilatation by increase on calcium influx, by activating TRPV3 channel | [13] | |
| Rat superior mesenteric artery | 10−8 to 3 × 10−4 M | Vasorelaxation by inhibition calcium influx through the L-type Cav, ROC and SOC channels | [53] | |
| Atria isolates | 10 μM and 100 μM | Negative inotropic and chronotropic effect | [53] | |
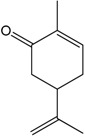 Carvone |
Rat thoracic aorta | 100 μM | Vasorelaxation by blocking calcium influx through VDDC | [60] |
| Rat thoracic aorta and trachea of guinea pigs | 10−6 to 3 × 10−4 M | Vasorelaxant effect | [61] | |
| Rat thoracic aorta | 10−7, 10−6, 10−5, and 10−4 g/mL | Vasodilatory effect by inhibiting both Ca2+ influx and Ca2+ release | [43] | |
| Porcine coronary artery | 32–320 μM | Vasorelaxation by inhibiting Ca2+ sensitivity and Ca2+ influx | [42] | |
| Ventricular cardiomyocytes and vascular smooth muscle cells | 0.01–1000 μM | Vasorelaxing action by inhibiting L-type Ca2+ channels and possible participation of TRPA1 | [44] | |
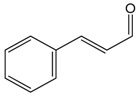 Cinnamaldehyde |
Rat aorta artery and Human | 10 μM | Prevents endothelial dysfunction by attenuating ROS generation and | |
| umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) | preserving nitric oxide levels and Nrf2 activation and the up-regulation of downstream target proteins | [40] | ||
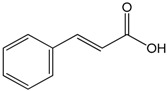 Cinnamic acid |
Rat thoracic Aorta | 0.1 mM, 0.2 mM, 0.4 mM, 1 mM, and 2 mM | Vasodilation via the NO–cGMP-PKG pathway, which stimulates Ca2+-activated K+ channels | [46] |
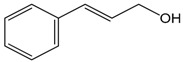 Cinnamyl alcohol |
Rat thoracic aorta artery | 0.2 mM, 0.4 mM, 0.6 mM, 1 mM or 1.5 mM | Vasodilation by activation of K+ channels and inhibition of Rho-kinase, which inhibit Ca2+ sensitization via the NO-cGMP-PKG pathway | [47] |
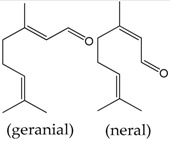 Citral (= geranial + neral) |
Rat thoracic Aorta artery | 0.6 to 6 mM | Vasorelaxation by reduced the calcium influx by the blockade of voltage dependent L-type Ca2+ channels | [68] |
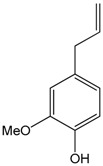 Eugenol |
Rat atria Muscle | 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10 mM | Increase in resting tension by cooperative activation of cardiac thin filaments by strongly attached cross-bridges (rigor state) | [63] |
| Rat atria Muscle | 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10 mM | Increase in resting tension by cooperative activation of cardiac thin filaments by strongly attached cross-bridges (rigor state) | ||
| Rat thoracic aorta artery | 1, 10 and 100 μmol L−1 | Vasorelaxant effect via inhibition of ROS and stimulation of NOS | [52] | |
| Rat thoracic aorta artery | 100 μM | Vasorelaxation by inhibiting ROS and elevating NO | [60] | |
| Rat cerebral artery | 100 μM | Vasorelaxation by inhibiting voltage-dependent Ca2+ | [63] | |
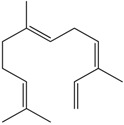 Farnesene |
Porcine splenic artery and coronary artery | 3, 10 and 30 μM | Vasodilatation by inhibiting calcium influx | [51] |
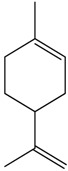 Limonene |
Rat thoracic aorta and trachea of guinea pigs | 10−6 to 3 × 10−4 M | Vasorelaxant effect | [61] |
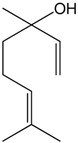 Linalool |
Rat thoracic aorta | 500 μM | Vasorelaxation by activating sGC and K+ channels and by inhibiting Ca2+ influx | [73] |
| Rat thoracic aorta | 100 μM | Vasorelaxation by blocking voltage dependent calcium channel (VDCC) and elevating NO | [60] | |
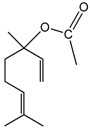 Linalyl acetate |
The mouse vascular smooth muscle cell line MOVAS-1 (MOVAS) and human umbilical vein endothelial cell line EA.hy926 (EA) | 0.01% v/v | Increase the intracellular K+ levels | [74] |
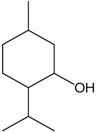 Menthol |
Rat aorta, mesenteric and coronary arteries | 0.01-1 mM | Vasorelaxation through inhibiting Ca2+ influx via nifedipine-sensitive Ca2+ channels in vascular smooth muscle | [76] |
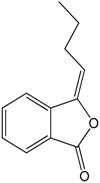 N-Butylidenephtalide |
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) | 20–50 μg/mL | Anti-angiogenic activities by increase of maintaining cell cycle on G0–G1 phase, and promoting apoptosis | [77] |
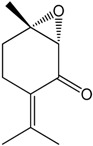 Rotundifolone |
Rat superior mesenteric artery | 10−7 to 3 × 10−3 M | Vasorelaxation through activation of BKCa channels and by the inhibition of Ca2+ entry through L-type Ca2+ channels | [81] |
