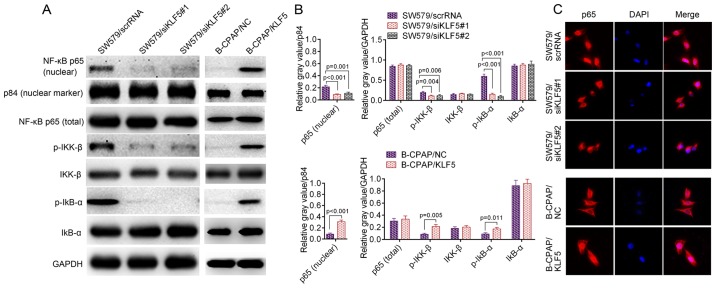
Figure 5.
(A) Western blotting of p-IκB-α, p-IKK-β and nuclear NF-κB p65 in SW579 cells (SW579/scrRNA, SW579/siKLF5#1 and SW579/siKLF5#2, left panel) and B-CPAP cells (B-CPAP/NC and B-CPAP/KLF5, right panel); and p84 was used as a nuclear marker. (B) Quantified western blotting results. (C) Immunofluorescent staining of NF-κB p65 in SW579/scrRNA, SW579/siKLF5#1, SW579/siKLF5#2, B-CPAP/NC and B-CPAP/KLF5 cells. NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; p-, phosphorylated-; IKK-β, inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase subunit β; IκB-α, nuclear factor of κ light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, α; scrRNA, scrambled RNA; si, small interfering RNA; NC, negative control; KLF5, Kruppel-like factor 5.