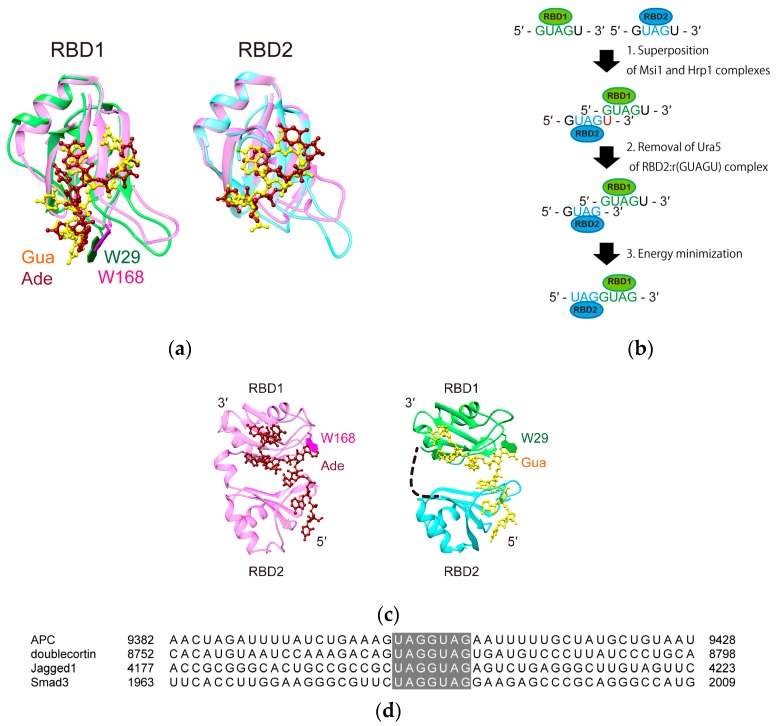
Figure 5.
A model structure of Msi1 RBD1-2 bound to the minimal target sequence, r(UAGGUAG). (a) Consecutive RBDs, RBD1-2, of Hrp1 (Lys156-His322), which are connected by a short linker (Ile234–Gly243), reportedly binds to r(UAUAUAUA). The structures of the Msi1 RBD1:r(GUAG) complex (green and yellow) and Hrp1 RBD1:r(AUAU) complex (pink and red) (left), and those of the Msi1 RBD2:r(UAG) complex (cyan and yellow) and Hrp1 RBD2:r(UAU) complex (pink and red) (right) are superimposed. Note that in both pairs, the binding regions are superimposed very well. One of the characteristic interactions between Msi1 RBD1 and r(GUAG), stacking of the aromatic rings of W29 and Gua1, was similarly found in the Hrp1 RBD1:RNA complex (W168 and Ade4) (labeled in the Figure); (b) A schematic illustration of the model building steps; (c) On the basis of the similarities found in (a), we used the solution structure of the Hrp1:r(UAUAUAUA) complex (PDB ID: 2CJK) (left) as a template and built a model structure containing the both RBDs of both Msi1 and r(UAGGUAG) (right). The W29 in Msi1 and W168 in Hrp1 are shown as green and magenta sticks, and labelled, respectively; (d) Alignment of the 3′-UTR regions of the Msi family target mRNAs, containing the r(UAGGUAG) sequence (highlighted in grey): H. sapiens APC (accession code NM_001127511.2), H. sapiens doublecortin (NM_000555.3), H. sapiens Jagged 1 (NM_000214.2), and H. sapiens Smad3 (NM_005902.3).