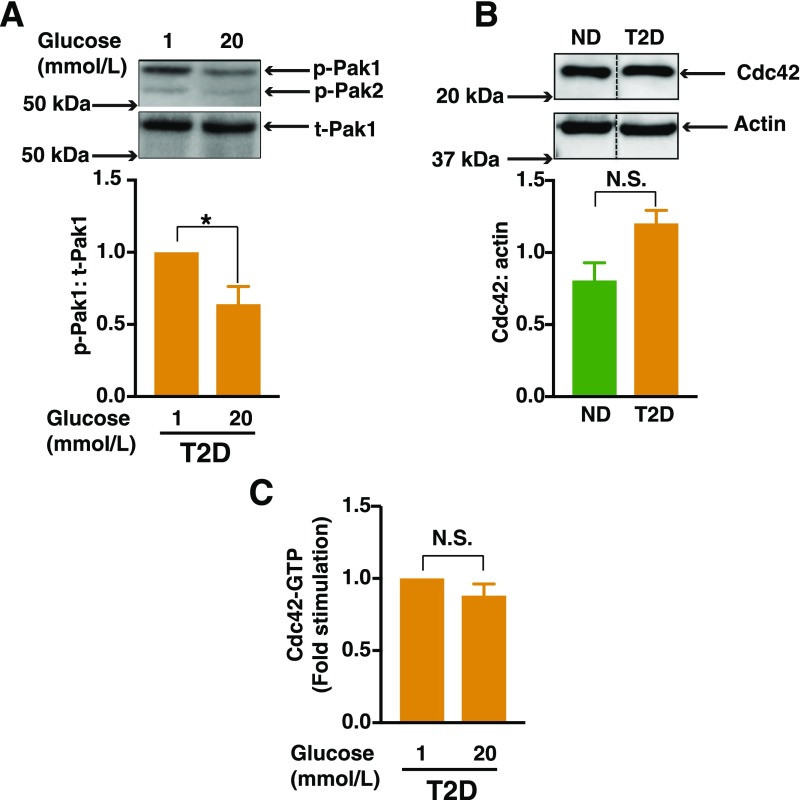
Figure 1.
Defective activation of Pak1 and Cdc42 in islets from human donors with T2D. A: Human T2D islets were allowed to recover for 2 h in CMRL media and were then further incubated for 1 h with KRBH prior to each experiment. Islets were then incubated in the presence of either a low (1 mmol/L) or high (20 mmol/L) glucose concentration for 5 min. Pak1 activity (phosphorylation of Pak1 [p-Pak1] Thr423) was normalized to total Pak1 (t-Pak1) protein content by Western blot analysis. Densitometry analysis of n = 3 independent experiments, shown as the mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05 vs. 1 mmol/L glucose concentration. B: Cdc42 expression from islets from humans without diabetes (ND) (n = 5) or islets from humans with T2D (n = 5). Densitometry analysis of n = 5 independent experiments, shown as the mean ± SEM; black vertical dashed lines indicate the splicing of lanes from within the same gel exposure. C: T2D islets incubated either in the presence of low (1 mmol/L) or high (20 mmol/L) glucose for 2 min prior to their lysis. Cdc42-GTP was quantified by the G-LISA method. Data represent the mean ± SEM from n = 3 independent experiments. P > 0.05. N.S., not significant.