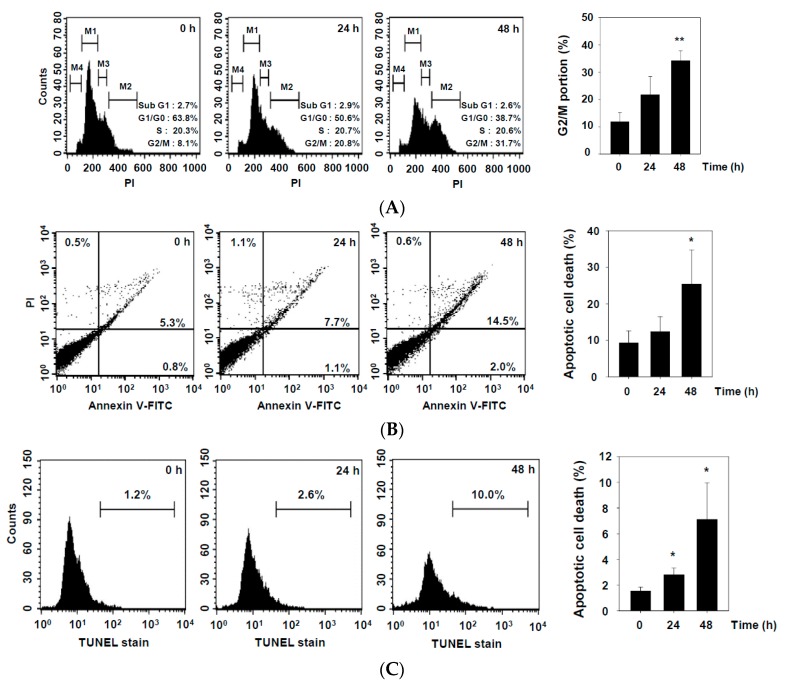
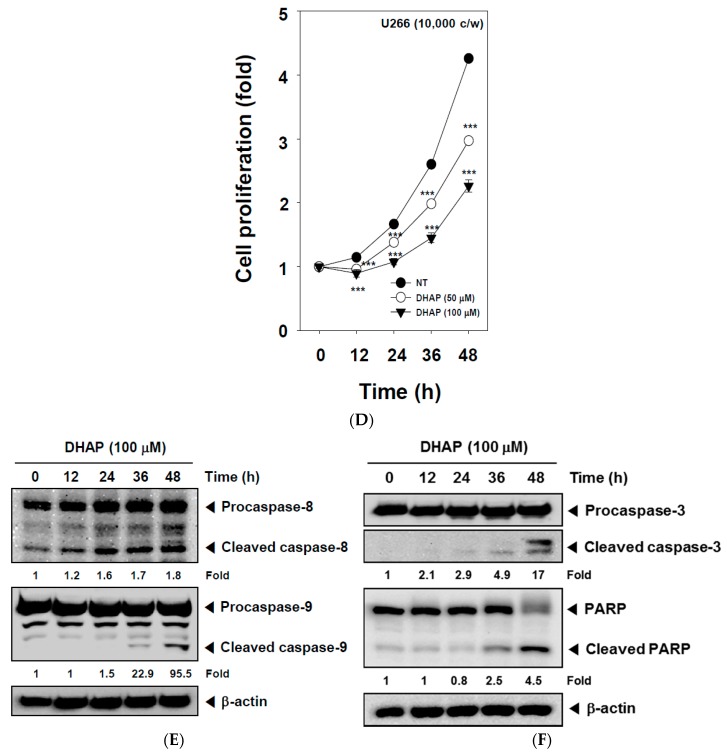
Figure 2.
Effect of DHAP on apoptosis and proliferation of U266 cells. The cells were treated with 100 μM of DHAP for 24 h and 48 h. (A) Cellular DNA staining incorporating PI and flow cytometric analysis was performed to ascertain the cell cycle distribution; (B) The cells were incubated with an FITC-conjugated Annexin V, then examined for an early apoptotic effect with flow cytometry; (C) The cells were fixed and incubated with a TUNEL reaction solution, then examined for DNA fragmentation with flow cytometry; (D) U266 cells were treated with 50 and 100 μM of DHAP, then subjected to an MTT assay after 12, 24, 36, and 48 h, to enable cell proliferation to be examined; (E) U266 cells were treated with 100 μM of DHAP for the time periods stated; whole-cell extracts were then prepared and examined via Western blot analysis for caspase-8 and caspase-9; (F) U266 cells were treated with 100 μM of DHAP for the time periods stated; whole-cell extracts were then prepared and analyzed via Western blot analysis for caspase-3 and PARP. To confirm equal protein loading, the immunoblot was stripped and reprobed for β-actin. Densitometric quantitation in fold change of each band has been indicated below the gel. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, vs. control.