Figure 2.
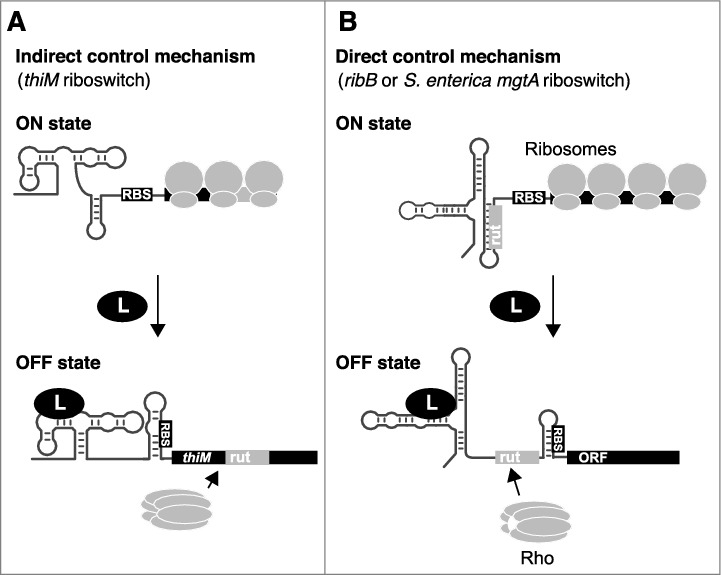
Indirect and direct control mechanisms used to regulate mRNA levels. A) The indirect control mechanism primarily relies on the modulation of translation initiation. Upon translation inhibition, a rut becomes accessible to Rho binding, leading to transcription termination. B) The direct control mechanism is performed by directly modulating the access of rut, which is dictated by ligand-dependent riboswitch conformational changes. Both indirect and direct control mechanisms rely on the inhibition of ribosome binding to the RBS in the ligand-bound state.
