Figure 2.
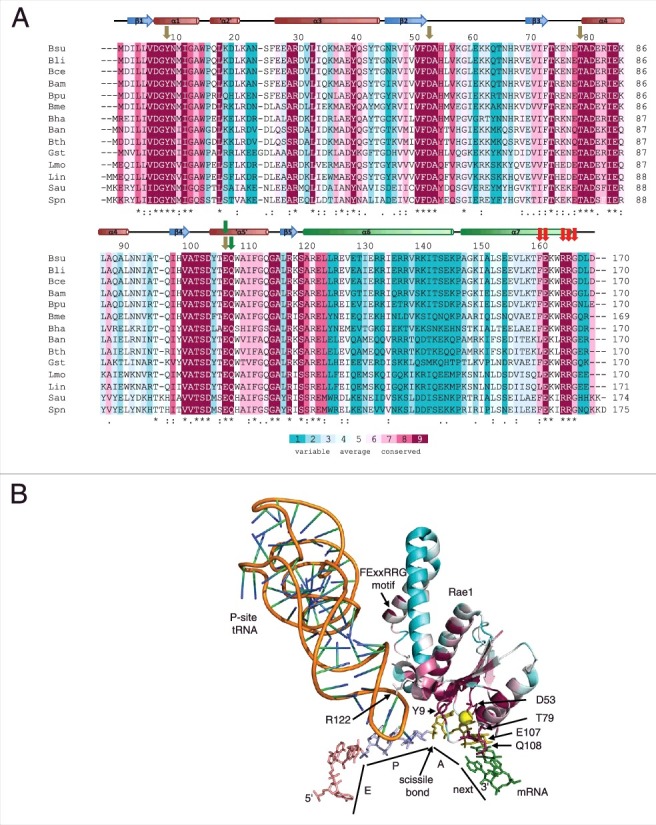
Conserved residues in Rae1. (A) Clustal Omega [19] alignment of 14 Firmicute Rae1 proteins. The alignment is color-coded according to an alignment of 500 non-identical sequences with Consurf [17]. The secondary structure of the Rae1 protein is shown above the alignment, with the two C-terminal helices shown in green. Abbreviations are as follows: Bsu, Bacillus subtilis; Bli, Bacillus lichiniformis; Bce, Bacillus cereus; Bam, Bacillus amyloliquifaciens; Bpu, Bacillus pumilus; Bme, Bacillus megaterium; Bha, Bacillus halodurans; Ban, Bacillus anthracis; Bth, Bacillus thuringiensis; Gst, Geobacillus stearothermophilus; Lmo, Listeria monocytogenes; Lin, Listeria innocua; Sau, Staphylococcus aureus; Spn, Streptococcus pneumoniae. Olive colored arrows show residues potentially involved in A-site codon recognition, green arrows point to amino acids potentially involved in interactions with the next codon and red arrows identify residues potentially involved in 50S subunit interactions. (B) Structure of Rae1 docked in A-site showing positions of conserved residues color-coded as in panel (A). The P-site tRNA is shown as an orange ribbon. The exit site (pink), peptidyl-transfer site (blue), acceptor site olive) and next (green) codons in the mRNA are labeled as E, P, A and next, respectively. The site of Rae1 cleavage is shown. Relevant amino acids for the potential A-site, next codon, P-site tRNA and 50S subunits interactions are labeled.
