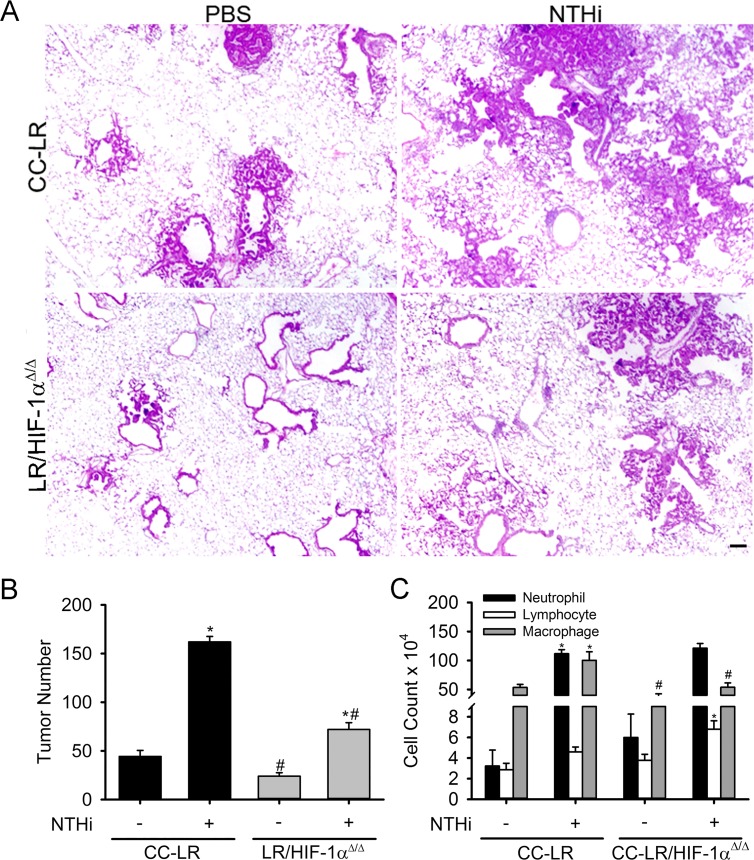
Figure 2. Lack of HIF-1α in the airway epithelium suppresses K-ras induced lung tumorigenesis and its promotion by inflammation.
CC-LR and LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ mice were exposed to an NTHi lysate aerosol starting at age 6 weeks weekly for 8 weeks to induce COPD-like airway inflammation. (A) Histopathological appearance of lung tissue from CC-LR and LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ in the absence or presence of COPD-type airway inflammation at age of 14 weeks (4× magnification, scale bar = 10 μm, applicable to all panels). (B) Lung surface tumor number in CC-LR and LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ mice in the absence or presence of COPD-type airway inflammation at age of 14 weeks (mean ± SE; *, P < 0.05 for CC-LR or LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ with NTHi exposure vs. without NTHi exposure; #, P < 0.05 for CC-LR without NTHi exposure vs. LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ without NTHi exposure or CC-LR with NTHi exposure vs. LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ with NTHi exposure; n = 12). (C) Lineage-specific leukocyte numbers in BALFs of CC-LR and LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ mice 1 day after last NTHi aerosol exposure at age of 14 weeks (mean ± SE; *, P < 0.05 for CC-LR or LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ with NTHi exposure vs. without NTHi exposure; #, P < 0.05 for CC-LR without NTHi exposure vs. LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ without NTHi exposure or CC-LR with NTHi exposure vs. LR/HIF-1αΔ/Δ with NTHi exposure; n = 6).