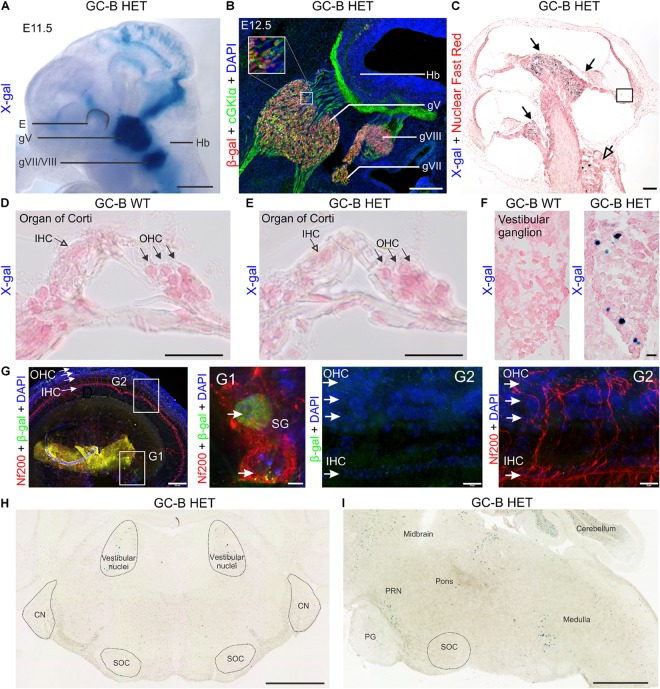
FIGURE 1.
Expression mapping of GC-B in the inner ear by X-gal staining using the Npr2-lacZ reporter and by immunofluorescent detection of β-gal. (A) β-Gal activity in Npr2lacZ/+ reveals sites of GC-B expression. Due to the presence of a nuclear localization signal, β-gal activity in the Npr2-lacZ reporter line is restricted to the nuclei of GC-B expressing cells. X-gal staining in Npr2lacZ/+ whole-mount embryo preparations at embryonic day (E) E11.5 shows a strong expression of GC-B in all cranial sensory ganglia (CSGs) (Ter-Avetisyan et al., 2014), including the trigeminal (gV) and acousticofacial ganglion (gVII/VIII). (B) Immunofluorescent detection of β-gal, co-immunostained with cGKIα, in parasagittal sections of the hindbrain region from E12.5 Npr2lacZ/+ embryos shows an overlapping distribution of β-gal with cGKIα expression in the CSGs at the level of CSG gV (trigeminal), gVII (facial), gVIII (vestibuloacoustic) and cGKIα expression in cranial sensory axons. (C) Cochlear section of a 10 week-old GC-B HET mouse stained for X-gal (blue) and Nuclear Fast Red (red) with the apex oriented upwards. X-gal-positive cells in GC-B HET mice are indicated by filled (SGNs) or open (vestibular ganglion neurons) arrows. (D,E) No X-gal staining was found in the organ of Corti, neither in inner hair cells (IHCs) nor outer hair cells (OHCs) (E shows a magnification from boxed areas in C). IHCs are indicated by open arrowheads and OHCs by filled arrowheads. (F) X-gal staining of sections from vestibular ganglia show a number of X-gal positive nuclei in the inner ear of GC-B HET mice (right panel). (G) Whole-mount preparations of an adult GC-B HET mouse immunohistochemically stained with anti-Nf200 (red) and anti-β-gal (green). (G1) and (G2) show a magnification of boxed areas for spiral ganglion neurons (SG) and organ of Corti, respectively. (H) Frontal and (I) sagittal sections of a P15 mouse brain show no X-gal staining in auditory brainstem regions (SOC, NC). Positive X-gal staining appears in the regions of vestibular ganglia and in regions related to the pontine reticular nuclei (PRN), close to the pontine gray (PG), and in the hindbrain (medulla). E, eye; g, ganglion; Hb, hindbrain. Nuclei in (B,G) were stained with 4′,6-diamidin-2-phenylindol (DAPI; blue). Scale bars: 1 mm (A); 25 μm (B); 100 μm (C); 25 μm (D–F); 100 μm (G left); 10 μm (G1,G2); 1 mm (H,I).