FIGURE 3.
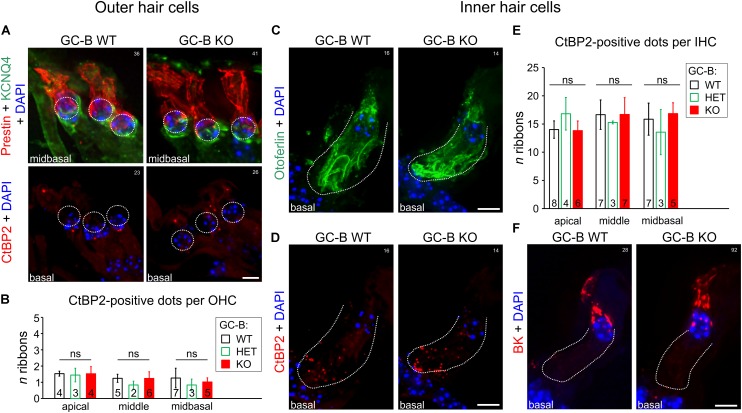
No change in inner hair cell (IHC) or outer hair cell (OHC) phenotype or reduction in numbers of afferent synaptic contacts with OHCs or IHCs was observed in GC-B KO mice. (A) Representative immunohistochemical staining of OHCs of GC-B WT (left panels) and GC-B KO (right panels) mice with antibodies targeted against KCNQ4 (green; upper panels) and prestin (red; upper panels) shown for midbasal cochlear turns. GC-B WT and GC-B KO OHCs did not differ in OHC marker protein expression. No differences for the OHC synaptic ribbons (red; CtBP2; lower panels) was observed. (B) Quantification of OHC ribbons in apical, middle, and midbasal cochlear turns. Number of OHC synaptic ribbons did not significantly vary between genotypes in the three studied cochlear turns. Bars in (B) represent mean ± SD ribbons per OHC; numbers in bars indicate the n of mice studied. Representative immunohistochemical staining of IHCs of GC-B WT (left panels) and GC-B KO mice (right panels) with antibodies against otoferlin (C, green), CtBP2/RIBEYE (D, red), and BK (F, red) shown for midbasal cochlear turns. Overall otoferlin staining, number of IHC synaptic ribbons (CtBP2), and BK expression were not different between genotypes. (E) Quantification of IHC ribbons in cochlear divisions of apical, middle, and midbasal turns representing low, middle and high frequency coding IHCs, respectively. No significant difference in number of synaptic ribbons was found between genotypes for either cochlear turn. Bars in (E) represent mean ± SD ribbons per IHC, numbers in open bars indicate the n of mice from which the IHC ribbons were counted from. Nuclei in (A,C,D,F) were stained with 4′,6-diamidin-2-phenylindol (DAPI; blue). Scale bars in (A,C,D,F): 5 μm. White numbers 14–41 indicate experiment numbers.