Figure 5.
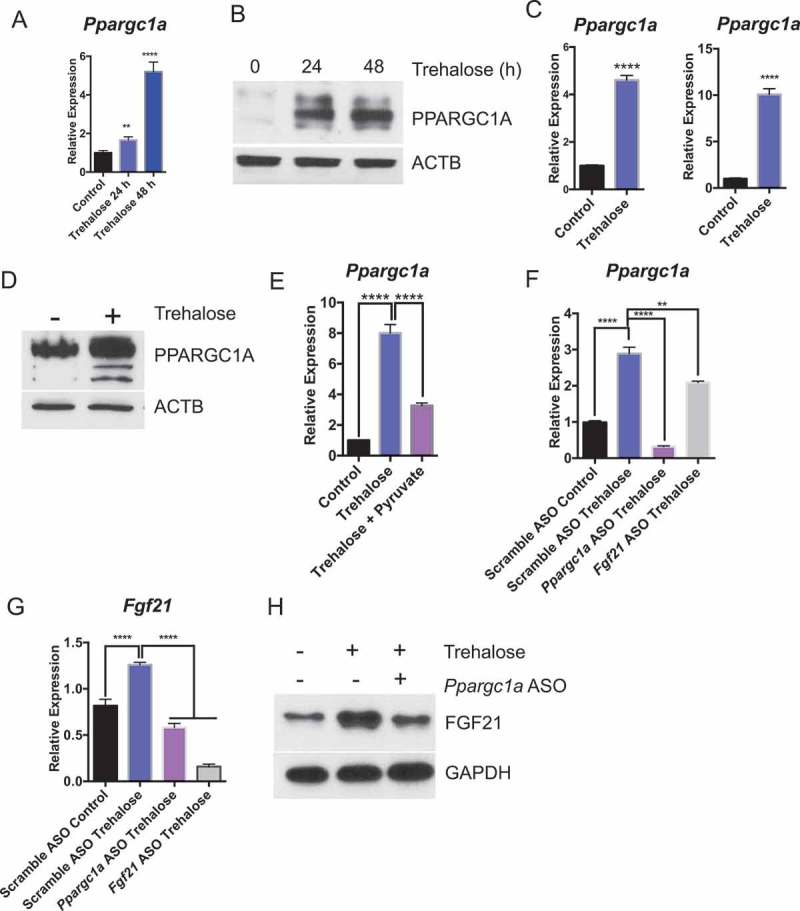
Trehalose activates hepatocyte PPARGC1A upstream of FGF21. (A) Ppargc1a mRNA accumulation in mice treated with trehalose 0–48 h with 3% trehalose water ad libitum (n = 4 mice per group). (B) PPARGC1A immunoblot showing hepatocyte PPARGC1A in mouse livers after 96 h treatment with sterile water (group labeled ‘0 h trehalose’) or 24–48 h treatment with 3% trehalose water. (C) Ppargc1a mRNA accumulation in primary hepatocytes treated with or without trehalose for 24 h. (D) PPARGC1A immunoblot showing hepatocyte PPARGC1A after 24 h trehalose exposure in regular growth media. (E) Ppargc1a mRNA accumulation in primary hepatocytes treated with or without trehalose in the presence or absence of 5 mM pyruvate. (F) Ppargc1a mRNA accumulation in primary hepatocytes treated with or without trehalose in the presence or absence of scrambled, Ppargc1a-, or Fgf21-directed antisense oligonucleotides (ASO). (G) Fgf21 mRNA accumulation in primary hepatocytes treated with or without trehalose in the presence or absence of scrambled or Ppargc1a- or Fgf21-directed ASOs. (H) FGF21 protein accumulation in primary hepatocytes treated with or without trehalose in the presence or absence of scrambled or Ppargc1a-directed ASO. GAPDH is used as a loading control. *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 versus control by Student’s T-test with Bonferroni-Dunn post-hoc correction for multiple tests.
