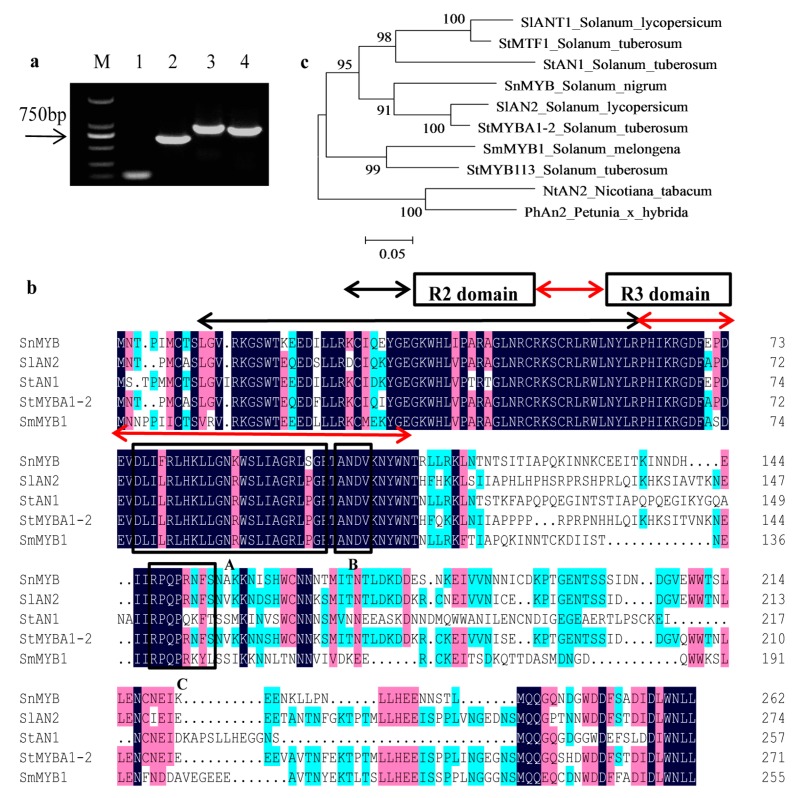
Figure 4.
Isolation of SnMYB and sequence alignment with other anthocyanin R2R3-MYB regulators from Solanaceae plants. (a) Cloning of SnMYB gene with rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE)-PCR. M: DL2000 DNA marker; lane 1: a 115-bp fragment of conserved region; lane 2: a 564-bp 5′ cDNA fragment with 5′RACE; lane 3: an 844-bp 3′ cDNA fragment with 3′RACE; lane 4: a 792-bp full-length coding sequence of SnMYB; (b) Protein sequence alignment of SnMYB with other anthocyanin-related MYB regulators from Solanaceae plants. The R2 and R3 repeat domains are indicated by black and red arrows, respectively. Box-A indicates the conserved region of the basic-Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) interacting motif ([DE]Lx2[RK]x3Lx6Lx3R). Box-B indicates a conserved motif [A/S/G]NDV in the R2R3 domain for dicot anthocyanin-promoting MYBs. Box-C indicates a C-terminal-conserved motif [R/K] Px[P/A/R]xx[F/Y] for anthocyanin-regulating MYBs; (c) Phylogenetic relationship analysis of SnMYB and known anthocyanin-related MYB regulators from other Solanaceae species. Sequences were aligned using DNAMAN version 4.0. Phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analysis was carried out using MEGA version 5.1. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method and 1000 bootstrap replicates.