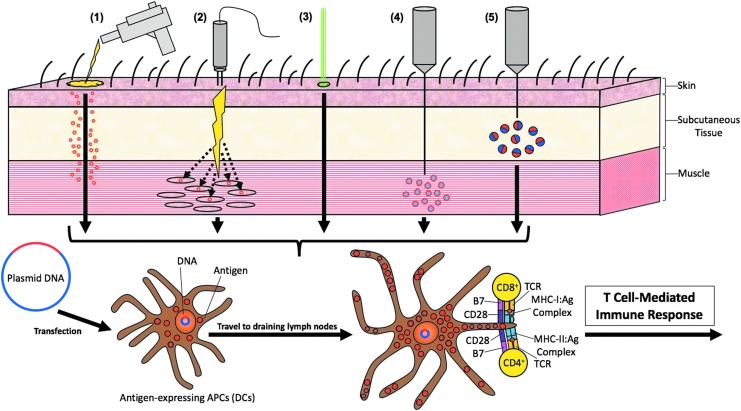
Figure 3.
Routes of administration. Different routes of administering DNA vaccines have been established to enhance antigen uptake by DCs in order to enhance T-cell-mediated immune response by both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells. (1) DNA vaccines can be delivered intradermally and subdermally through a gene gun. In this process, the biological and ballistic instrument delivers HPV DNA-coated gold particles directly into immature DCs located under the skin (i.e., Langerhans cells). (2) HPV DNA vaccines can also be injected intramuscularly followed by electroporation in order to enhance antigen expression in muscle cells. This will allow for inflammatory responses in local myocytes, leading to the antigens to be taken up by DCs. (3) HPV DNA uptake by DCs can also be enhanced through intradermal administration followed by laser treatment. (4) HPV DNA can also be delivered via intramuscular injection encapsulated in microspheres and nanoparticles in order to enhance the uptake of the vaccine by DCs. (5) There are other novel delivery systems to enhance DNA vaccine potency such as subcutaneously injecting HPV DNA mixed with PEI600-Tat.