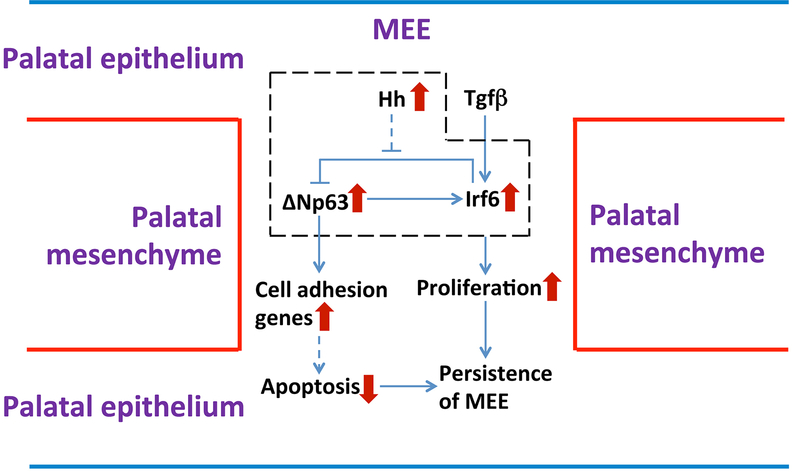
Figure 7. Schematic diagram of the mechanism underlying the persistence of the MEE in K14-Cre;R26SmoM2 mice.
Constitutive activation of Hh signaling in the palatal epithelium affects the regulatory loop between p63 and Irf6, causing the failure of p63/Irf6-dependent cell cycle exit, which may result in the persistence of the MEE in K14-Cre;R26SmoM2 mice. Maintenance of p63 expression in SmoM2 mutant MEE may prevent apoptosis in MEE cells through enhanced cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion, which may also contribute to the persistence of the MEE in K14-Cre;R26SmoM2 mice.