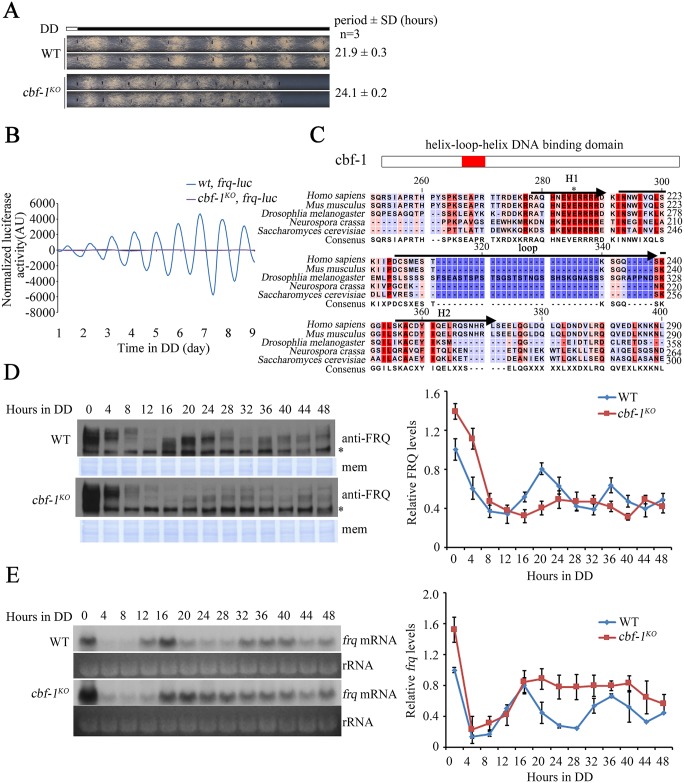
Fig 1. Deletion of the cbf-1 gene results in long period and low amplitude of circadian rhythms.
(A) Race tube analyses of the cbf-1KO strains. (B) Luciferase activity of wt, frq-luc and cbf-1KO, frq-luc strains. The low normalized luciferase signal levels in the cbf-1KO, frq-luc strain reflect the low-amplitude fluctuation of luciferase activity. Raw data were normalized to subtract the baseline calculated by LumiCycle analysis software. (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of the HLH domain from the Neurospora CBF-1, Saccharomyces CBF-1, Drosophila USF1, mouse USF1, and human USF1. The HLH domain is composed of H1, Loop and H2. The asterisk indicates the conserved Glu (E9) in the basic domains of HLH proteins. (D) Western blot analyses of the levels of FRQ protein in the wild-type and cbf-1KO strains. Asterisks indicate nonspecific bands. Samples were grown in DD for indicated hours before harvest. PVDF membrane stained with Coomassie blue (mem) was used as a loading control. Quantification of the levels of FRQ protein is shown beside the western blot. (E) Northern blot analyses of the levels of frq mRNA. Ribosome RNA (rRNA) bands stained by ethidium bromide shown below the northern blot acted as a loading control for each sample. Quantification of the levels of frq mRNA is shown beside the northern blot.