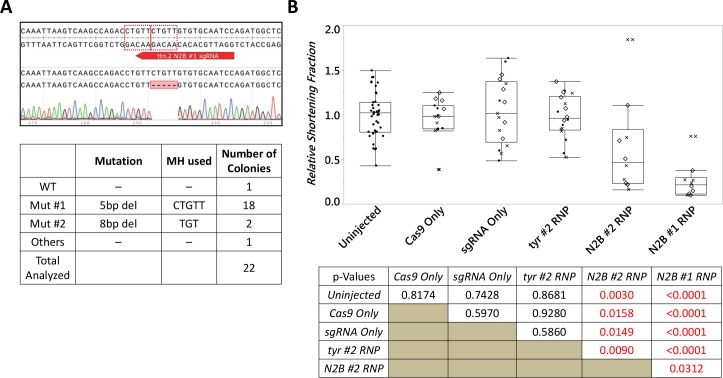
Fig 5. PreMA reagent against ttn.2 N2B results in specific reduction of shortening fraction in 2 dpf F0 zebrafish.
A. Top–Wildtype ttn.2 sequence at the N2B exon with sgRNA target site annotated in red. The dotted red boxes are MH arms predicted to be used most frequently. Raw sequence alignment of the whole PCR amplicon demonstrates that the majority of reads are the expected 5 bp deletion allele. Bottom–summary data from subcloning analyses. 86% of the mutant allele recovered were of the predicted MH allele. B. Previously reported pickwick phenotype was successfully recapitulated using this CRISPR-Cas9. 2 dpf zebrafish were immobilized in 3% methylcellulose for live recording of cardiac functions. Whereas injections with Cas9 only (660 pg), N2B #1 sgRNA only (300 pg), or tyr #2 sgRNA RNP (300 pg sgRNA + 660 pg Cas9) did not result in changes in shortening fraction at this age, MMEJ-inducing RNP injection targeting N2B #1 (300 pg sgRNA + 660 pg Cas9) resulted in a specific reduction in shortening fraction by 78.4%. In contrast, NHEJ-inducing RNP injection targeting N2B #2 (300 pg sgRNA + 660 pg Cas9) resulted in attenuated effects on shortening fraction (53.3% reduction), despite similarly high edit efficiency. Each data point represents an individual animal scored with the shape of the marker denoting unique experiment. N ≥ 3 biological and technical replicates, except for N2B #2 where N = 2. At least 5 injected animals were scored in each experiment. P-values calculated by Wilcoxon’s Each Pair Calculation (adjusted for multiple comparisons).