Figure 1.
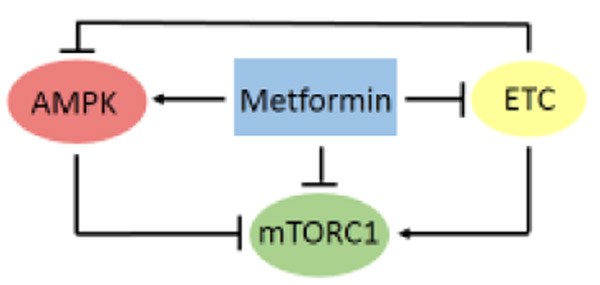
The Major Molecular Targets of Metformin. These are the ETC, AMPK, and mTORC1. ETC produces ATP, leading to AMPK downregulation. Metformin inhibits the ETC, resulting in reduced ATP synthesis. The elevated AMP/ATP ratio activates AMPK, which phosphorylates and inhibits mTORC1. The metformin-mediated inhibition of ATP synthesis also results in inhibition of mTORC1. Metformin also activates AMPK and inhibits mTORC1 by a mechanism that is independent of the ETC. Abbreviations: AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ETC, electron transport chain; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1.
