Figure 9.
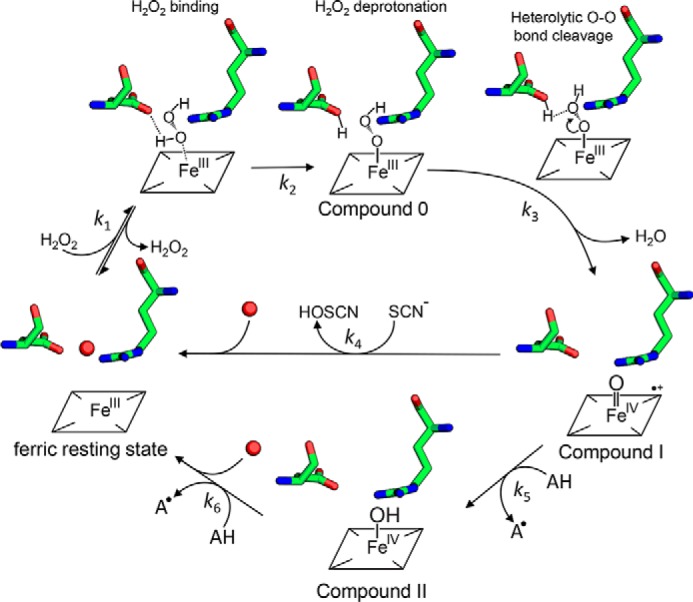
Proposed reaction mechanism for Compound 0, Compound I, and Compound II formation in B-class DyPs. Hydrogen peroxide enters the narrow distal heme access channel, binds (k1), and is deprotonated by Asp-143 (Compound 0 formation). Heterolytic cleavage of the O–O bond (k3) forms Compound I (oxoiron(IV) porphyrin radical) (k3), which is reduced by either two-electron donors like thiocyanate (−SCN) directly to the ferric resting state, thereby producing hypothiocyanite (HOSCN) (k4), or by one-electron donors like serotonin (AH) to Compound II (oxoiron(IV) species) (k5), thereby producing the corresponding radical (A•). Finally, a second one-electron donor (AH) reduces Compound II to the ferric resting state (k6).
