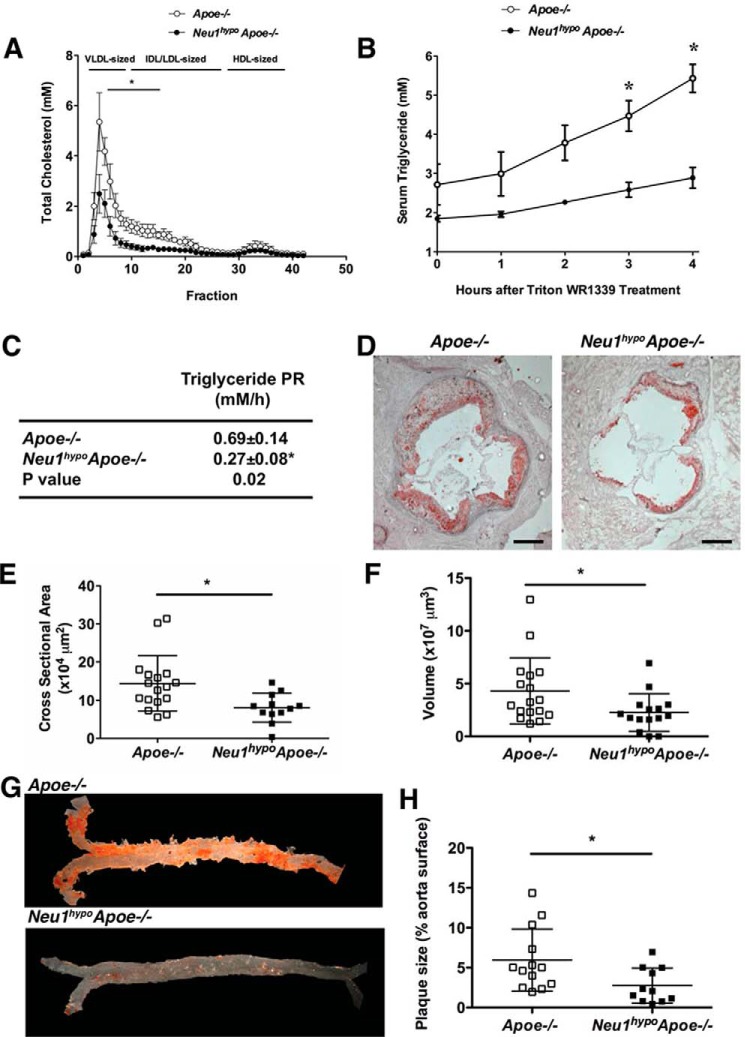
Figure 2.
FPLC cholesterol profiles, in vivo hepatic VLDL-TG secretion, and atherosclerotic lesion analysis for regular chow-fed Apoe−/− and Neu1hypoApoe−/− mice. A, the serum cholesterol FPLC profiling revealed a significant decrease in VLDL- and LDL-sized particles in 7-month-old, unfasted male Neu1hypoApoe−/− mice (n = 3) compared with Apoe−/− controls (n = 3). B, after fasting overnight, male Apoe−/− (n = 4) and male Neu1hypoApoe−/− mice (n = 4) were injected with Triton WR1339 (500 mg/kg). Serum samples were collected before injection (time 0) and at 1, 2, 3, and 4 h after Triton WR1339 administration. There was a significant decrease in the VLDL-TG concentration in the hypomorphic sialidase mice compared with controls. C, the in vivo hepatic VLDL-TG production rate, calculated by linear regression from the slope of the VLDL-TG level versus the time curve in B. There was a significant decrease in the hepatic VLDL-TG production rate (PR) in Neu1hypoApoe−/− mice compared with Apoe−/− mice. This difference indicates that hypomorphic sialidase expression decreased hepatic VLDL secretion. The values are displayed as mean ± S.E. D, representative cross-sections of the aortic sinus from male Apoe−/− and Neu1hypoApoe−/− mice fed a regular chow diet at 7 months of age. Sections were stained with Oil Red O for neutral lipids and counterstained with hematoxylin for nuclei. Scale bar = 200 μm. The atherosclerotic lesions were significantly reduced in male Neu1hypoApoe−/− mice (n = 15) compared with male Apoe−/− mice (n = 17) both in area (E) and volume (F). Individual data are displayed with mean ± S.D. G and H, representative Sudan IV staining of aortas from male Apoe−/− and Neu1hypoApoe−/− mice (G) and quantification of plaque size as a percentage of aorta surface (H). Plaque size was significantly reduced in the Neu1hypoApoe−/− mice (n = 11) compared with Apoe−/− mice (n = 10). *, p < 0.05.