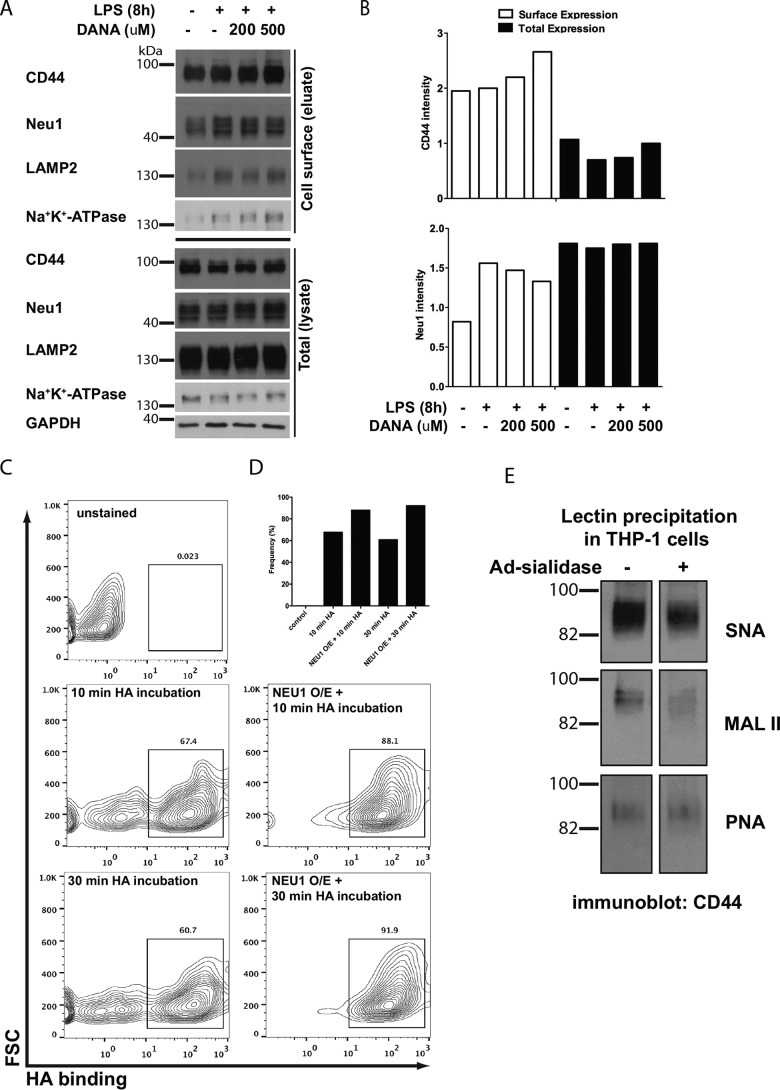
Figure 7.
NEU1 desialylation of CD44 leads to an increased proportion of THP-1 cells that bind hyaluronic acid. A, CD44 and NEU1 protein expression at the cell surface in untreated cells, 8-h LPS, 8-h LPS + 200 μm DANA, or 8-h LPS + 500 μm DANA. Controls included Na+-K+-ATPase for cell-surface protein, LAMP2 for lysosomal protein, and GAPDH for cytosolic protein. Cell-surface proteins were biotinylated, purified, and blotted for the various antibodies. B, quantification of CD44 and NEU1 expression at the cell-surface versus total cell expression. C and D, THP-1 cells infected with adenovirus-expressing human NEU1 sialidase (NEU1 O/E = NEU1 overexpression) bound more HA compared with uninfected cells. Unstained cells were used as a control. The proportion of cells binding HA was measured using the box indicated in C. E, sialylation of CD44 was examined following infection of THP-1 cells with adenovirus-expressing human NEU1 sialidase, by immunoprecipitation of protein using S. nigra (SNA) lectin (α2,6-linked sialic acid levels), M. amurensis lectin II (MALII) lectin (α2,3-linked sialic acid), or PNA lectin (binds underlying galactosyl (α-1,3) GalNAc structure), followed by probing lectin-precipitated protein with anti-CD44 antibody.