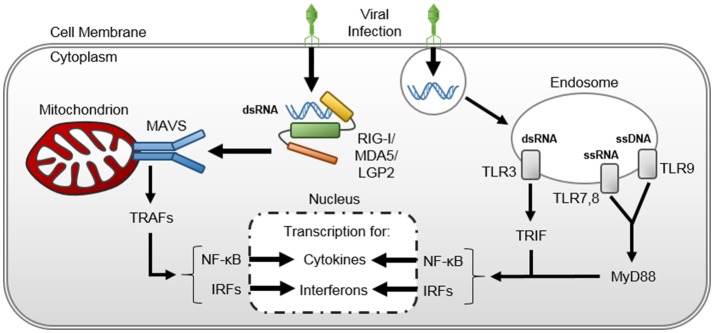
Figure 1.
Viral-induced cytokine upregulation and release. Double stranded viral ribonucleic acids are (dsRNA) recognized within the host cellular cytosol by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs)- RIG-I, MDA5, and LGP2. The RLRs bound to viral dsRNA undergo conformational change and complex with mitochondrial antiviral signaling (MAVS) protein on the mitochondrion surface. The RLR-MAVS interaction instigates an assembly of host proteins to activate TNF- receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), thereby inducing nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and interferon regulator factor (IRF)-mediated cytokine transcription in the host cell nucleus. Viral nucleic acids are also recognized within Toll-like receptors (TLRs) within host cell endosomes, triggering myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) and Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-domain-containing adaptor-inducing interferon-β (TRIF) pathways that also activate NF-κB and IRF-mediated cytokine transcription in the host cell nucleus.