Figure 3.
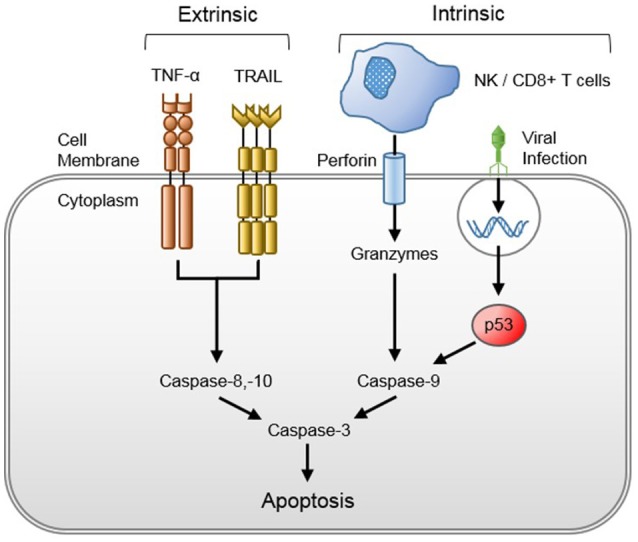
Viral-induced host cytotoxicity through the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is released after viral recognition by the innate immune system, and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is released from viral-reprogrammed macrophages, both of which bind their respective host cell surface death receptors to activate the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Natural killer (NK) and cluster of differentiation 8 (CD8+) T cells inject perforin into the membranes of infected host cells, through which they secrete granzymes that elicit the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. The intrinsic pathway may be activated after viral protein recognition by the host cell or suicide gene insertion by cytotoxic viruses.
