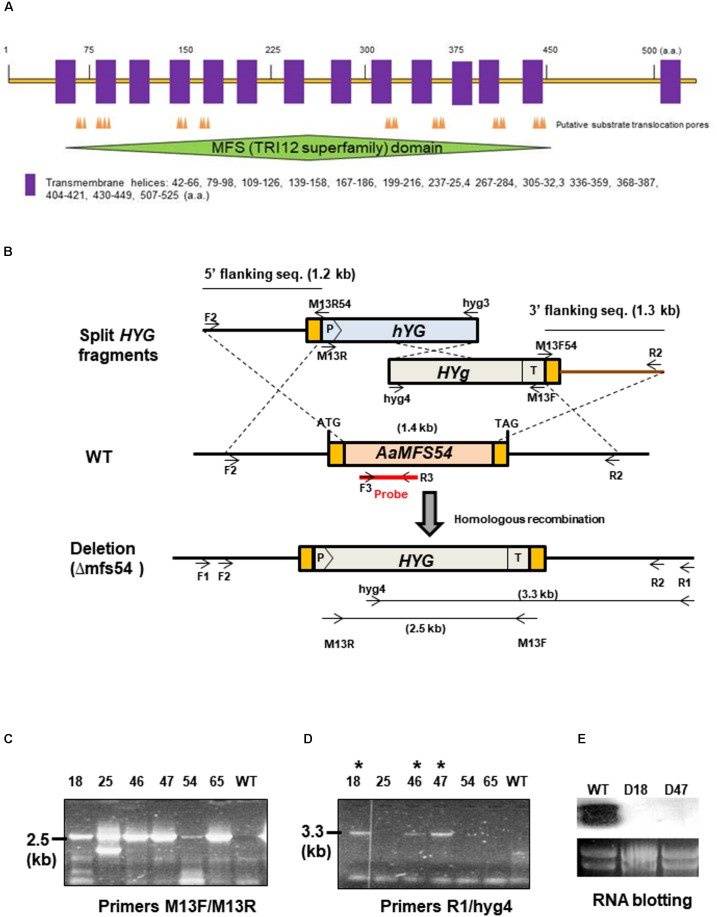
FIGURE 1.
Targeted disruption of AaMFS54 in the tangerine pathotype of Alternaria alternata using a split marker approach. (A) Functional domains and transmembrane helices found in the AaMFS54. (B) Schematic illustration of generation of truncated but overlapping hygromycin phosphotransferase gene (HYG) under control by the Aspergillus nidulans trpC promoter (P) and terminator (T) within AaMFS54. Oligonucleotide primers used to amplify AaMFS54 fragments and to label the probe are indicated. (C) Amplification of DNA fragments from genomic DNA of wild type (WT) and transformants with the primer M13F and M13R. (D) Amplification of DNA fragments from genomic DNA of wild type (WT) and transformants with the primer R2 paired with hyg4, indicating that AaMFS54 is deleted in transformants D18, D46, and D47 (indicated by ∗). (E) Northern blot hybridization of fungal RNA with an AaMFS54-specific probe reveals the lack of the AaMFS54 gene transcripts in both D18 and D47 strains.