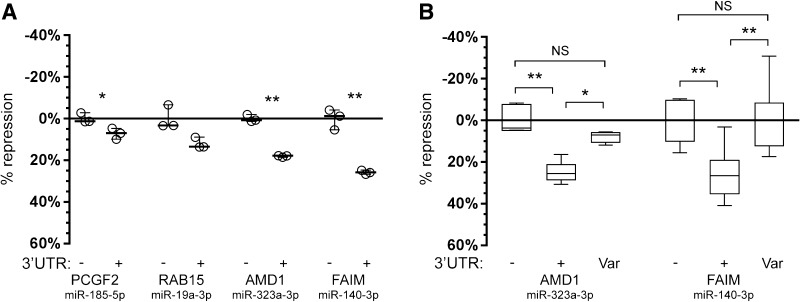
Fig. 2.
De novo variants identified in an ID cohort disrupt functional miRNA binding sites. a Luciferase reporter assays were performed to test the activity of the four predicted miRNA binding sites. Expression of the reporter was strongly (≥ ~ 20%) and significantly (p < 0.01) reduced in the presence of miRNA binding sites carrying the reference allele (+) of AMD1 and FAIM compared to an empty vector control (−). Significance was calculated using pairwise t test. Results are reported as average of three independent transfections and show the spread of data using the function “min to max” in GraphPad Prism7 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla California USA, http://www.graphpad.com). b Introduction of the variant allele identified in the ID patient (“Var”) for both the AMD1 and FAIM binding sites completely abolished repression by the cognate miRNA. Significance was calculated using an ANOVA test, followed by post hoc Tukey calculation. Data are displayed as the percentage of repression observed between the control condition which consists of an empty luciferase reporter with no miRNA binding sites (−) and inclusion of the reference allele (+) or the variant allele (Var). Results are reported as average of three biological replicates (each comprising three independent transfections) and show the spread of data using the function “min to max” in GraphPad Prism7. Statistical significance is indicated as: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01