FIG 3.
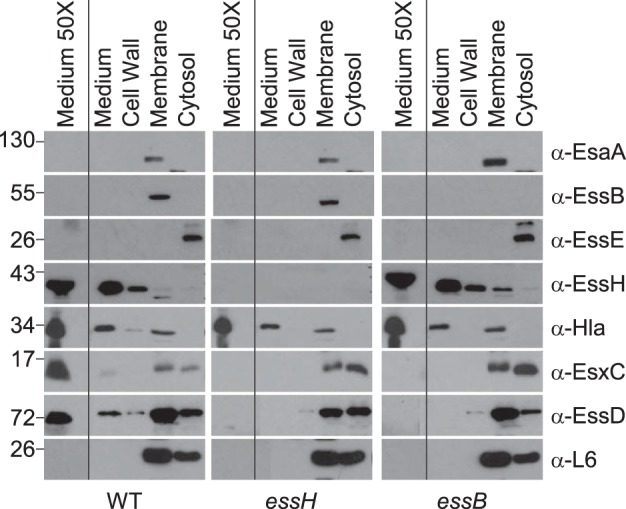
Mutations in essH and essB do not affect Sec protein secretion. Cultures of S. aureus USA300 LAC* WT and essH and essB mutants were grown to an A600 of 3.0 and centrifuged, and proteins in the extracellular medium (medium) were separated from the bacterial sediment. Sediments of 1-ml culture samples were fractionated by suspending staphylococci in sucrose buffer containing lysostaphin. The resulting protoplasts were sedimented by centrifugation. Proteins released by lysostaphin from the bacterial envelope (cell wall) were removed with the supernatant. Protoplasts were lysed and samples ultracentrifuged to sediment membrane proteins (membrane) and separate them from soluble proteins in the supernatant (cytosol). Proteins in all fractions were precipitated with TCA, separated by SDS-PAGE, electro-transferred to PVDF membrane, and analyzed by immunoblotting with rabbit polyclonal antibodies specific for Ess secretion machine components EsaA (α-EsaA), EssB (α-EssB), EssE (α-EssE), murein hydrolase EssH (α-EssH), α-hemolysin (α-Hla), ESS secretion substrates EsxC (α-EsxC), and EssD (α-EssD) as well as ribosomal protein L6 (α-L6). Samples of 50-ml cultures were centrifuged to sediment bacteria, and proteins in the culture medium were precipitated with TCA, washed with acetone, and suspended in sample buffer to generate a concentrated sample of proteins in the culture medium (medium 50×). Numbers on the left indicated kilodaltons.
