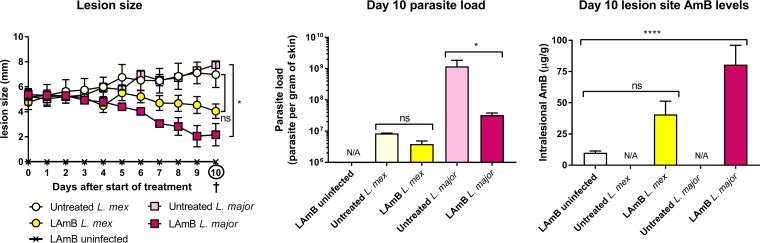
FIG 8.
Efficacy and biodistribution of liposomal amphotericin B LAmB) in murine models of L. major and L. mexicana (L. mex) CL. Mice were injected (s.c.) with parasite-free medium (uninfected) or infected with L. major or L. mexicana promastigotes in the rump skin. When a nodular lesion had formed at the inoculation site of CL-infected animals (10 and 30 days postinoculation for L. major and L. mexicana, respectively), animals received either 5% dextrose (untreated) or 25 mg/kg LAmB (i.v.) on days 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8. During treatment, lesion size (a) was measured daily. On day 10, lesion skin tissues were collected, and parasite load (b) and AmB levels (c) were determined. Each point represents the mean ± SEM (n = 3 to 5 per group). ANOVA (1-way for parasite load and intralesional AmB levels, repeated measures for lesion size), followed by Tukey's multiple-comparison test (*, P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant) were used. N/A, not applicable.