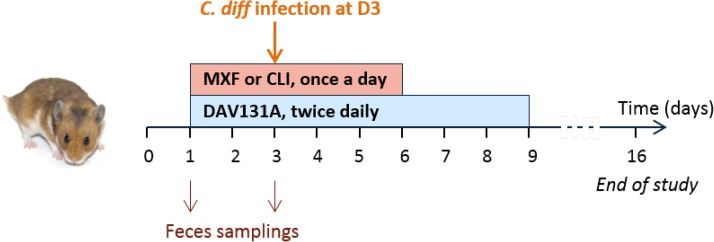
FIG 1.
Experimental design of the studies. Male Syrian golden hamsters were treated with moxifloxacin (MXF) (n = 70) or clindamycin (CLI) (n = 60) once a day by the subcutaneous route for 5 days and received various doses of DAV131A twice a day (b.i.d.) by the oral route for 8 days, which would result in the exposure of the microbiota to various antibiotic concentrations and different bacterial environments. The toxigenic C. difficile strain UNT103-1 was inoculated at D3. Fecal samples were obtained just before the beginning of treatment and at the third treatment day. Microbiota analysis was performed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing on both samples, and the fecal concentration of active antibiotic was determined at D3 by microbiological assay. Survival was monitored up to D16.