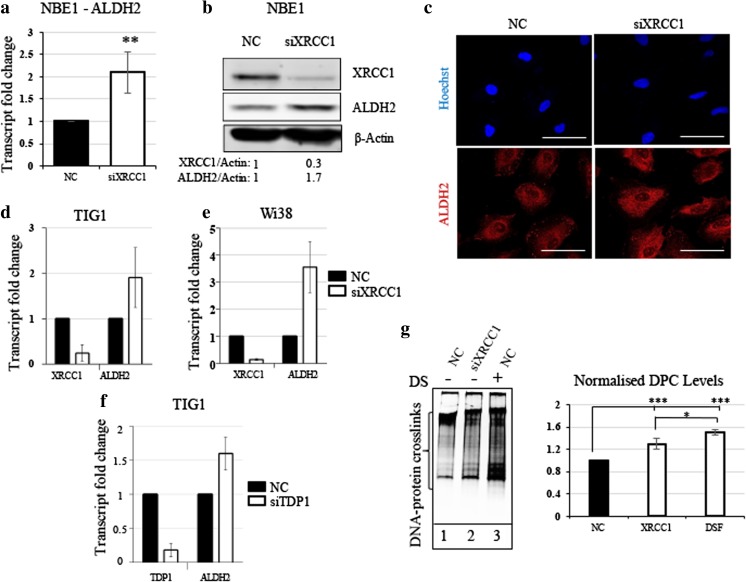
Fig. 1.
XRCC1 depletion causes an increased expression of ALDH2 and increased DNA-protein crosslinks. a qRT-PCR analysis of ALDH2 transcript levels in NBE1 cells after 72 h of XRCC1 knock down (KD). b Representative Western blot analysis of ALDH2 and XRCC1 levels in NBE1 cells after 72 h of XRCC1 KD. c Representative immunofluorescence analysis of ALDH2 in NBE1 cells after 72 h of XRCC1 KD. d qRT-PCR analysis of ALDH2 and XRCC1 transcript levels in TIG1 cells after 72 h of XRCC1 KD. e qRT-PCR analysis of ALDH2 and XRCC1 transcript levels in WI38 cells after 72 h of XRCC1 KD. f qRT-PCR analysis of ALDH2 and TDP1 transcript levels in TIG1 cells after 72 h of TDP1 KD. qRT-PCR reference genes are B2M and GAPDH for a, d and e, and TBP and GAPDH for f. g Left panel, representative silver staining analysis of protein crosslinked onto DNA in NBE1 cell extracts after 72 h of XRCC1 KD or 24 h of disulfiram treatment (DS, 10 μM). Right panel, densitometric quantification of the data. Data are expressed as mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001