Figure.
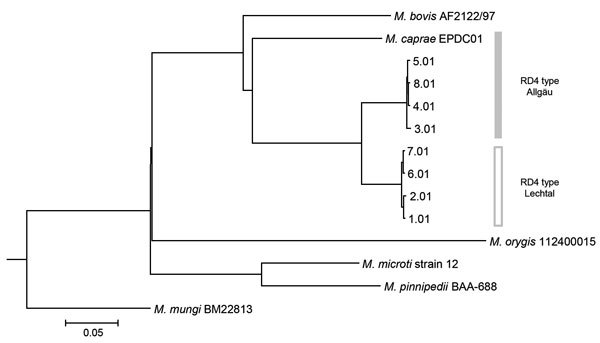
Phylogenetic tree of isolate EPDC01 from a captive Borneo elephant with Mycobacterium caprae infection, Japan, 2016, and 8 Mycobacterium caprae strains (Allgäu and Lechtal types) from a report by Broeckl et al. (13). Short reads of M. caprae strains were assembled by CLC Genomics Workbench version 9.5.1 (https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com/solutions/functional-genomics/?gclid=EAIaIQobChMIvvGL3L7T2wIVTSOBCh2FAAKtEAAYASAAEgKLWvD_BwE) before analysis. Core single-nucleotide polymorphisms of all 13 strains, including reference M. tuberculosis complex strains (M. bovis, AF2122/97 [GenBank accession no. NC_002945.4]: M. orygis, 112400015 [NZ_APKD00000000.1]: M. pinnipedii, BAA-688 [MWXB00000000.1]: M. microti, strain 12 [CP010333.1]: and M. mungi, BM22813 [NZ_LXTB00000000.1]), were determined and used for tree construction based on neighbor-joining by kSNP3 (12). A tree including all 61 strains described by Broeckl et al. (13) is shown in the Technical Appendix Figure. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
