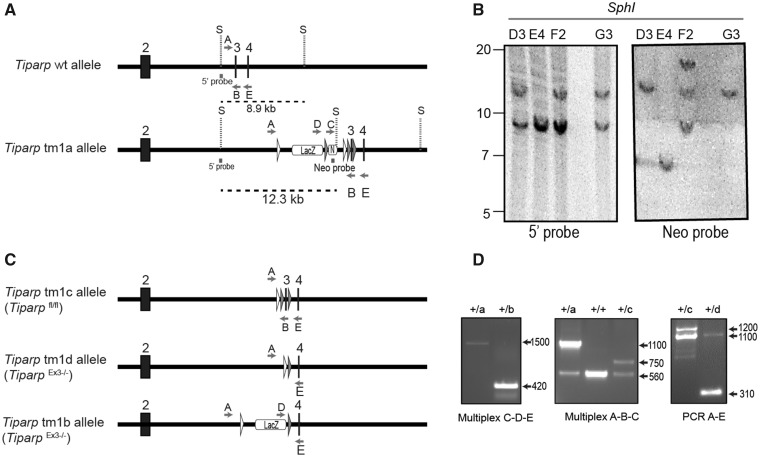
Figure 1.
Generation of the conditional Tiparpfl/fl mice. A, Schematic diagram of Tiparp WT allele and the allele with successful recombination of the tm1 targeting construct (Tiparp tm1a allele) and corresponding Southern blot data. Exon numbers reflect known coding exons; white arrowheads represent FRT sites; gray arrowheads represent LoxP sites; LacZ represents lacZ reporter gene; N represents the Neo resistance cassette; S, SphI site; dashed lines indicate the fragment of DNA generated by SphI digestion that was detected with the radiolabeled probes (5’ probe and Neo probe); letters indicate genotyping primers. B, Southern blots show Tiparp allele fragments detected with the radiolabeled probes: ES clones D3 and G3 show correct homologous recombination of the targeting construct (12.3 kb fragment detected with 5’ probe) without additional random integrations (only the 12.3 kb band detected with Neo probe). C, Schematic diagram of Tiparp tm1 alleles following excision of sequence by CRE or FLP recombinases. D, PCR data from mouse tail biopsies. The Tiparp tm1a allele was converted to tm1b using CRE recombinase to remove the Neo cassette and exon 3 located between the LoxP sites. Primer pair D-E amplify a product spanning the excision sites to show that the floxed sequences were removed (420 bp). The Tiparp tm1a allele was converted to tm1c using FLP recombinase to remove the LacZ and Neo cassettes located between the FRT sites. Primer pair A-B amplifies a product spanning the excision site to show that the sequence was flipped out (750 bp). The Tiparp tm1c allele was converted to tm1d using CRE recombinase to remove the floxed exon 3. Primer pair A-E amplify a product spanning the floxed region to show that the exon is removed (310 bp). Sample genotypes: + indicates the Tiparp WT allele; letters indicate the Tiparp tm1 corresponding allele (tm1a, tm1b, tm1c, and tm1d).