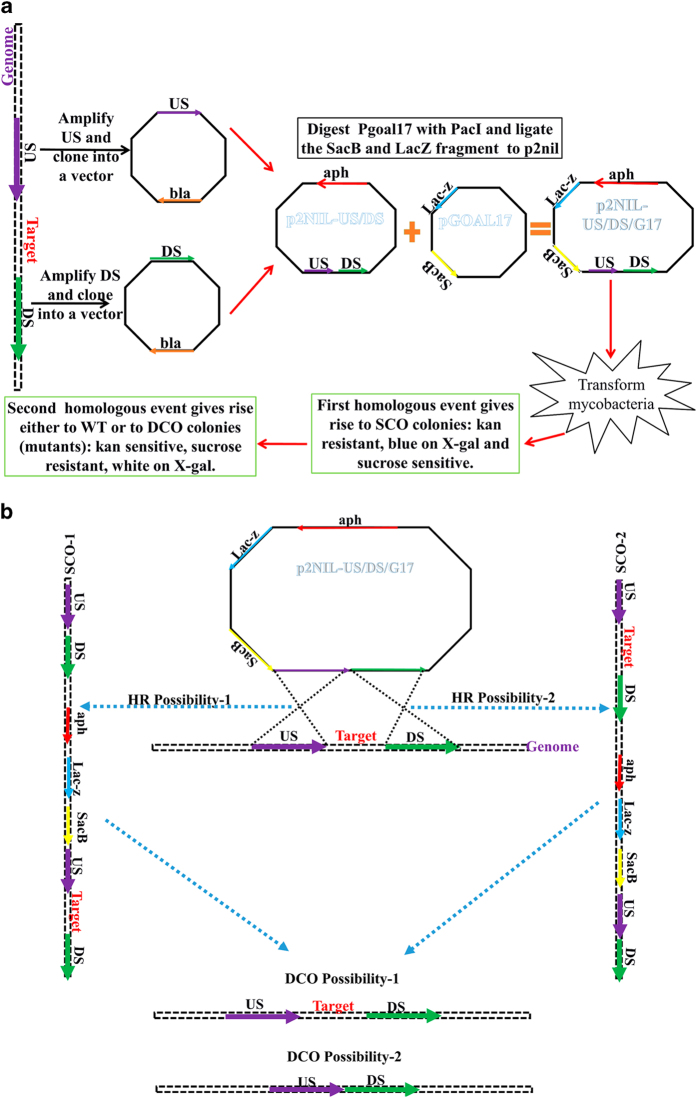
Figure 3. Gene deletion process adapted from previously described methods.
(a) The upstream and the downstream regions of the targeted gene were amplified and subsequently cloned separately into any commercially available sub-cloning vector. Next, these fragments were excised by restriction enzyme digestions (RED) from these vectors and simultaneously ligated into a p2NIL vector that was previously linearized by RED. Then the PacI fragment of Pgoal17 (containing the sacB gene coding for levan sucrose for sucrose sensitivity and Lac-z gene coding for the β-galactosidase which breaks down X-gal to yield a blue product) was ligated to the p2NIL vector linearized by PacI. After confirmation of the integrity of the resulting construct by RED and by sequencing, it was used to achieve gene deletion as indicated. (b) After transformation of mycobacteria with the designed construct, a homologous recombination (HR) event occurs between the US (HR-1) or DS (HR-2) to give rise to single cross over (SCO) colonies that have incorporated the entire plasmid into their genome. The second HR event occurs after sub-culturing these colonies without antibiotics, giving rise to either a wild-type strain, or a strain with the deleted gene. Deletion was thereby confirmed by PCR and southern blotting analyses. Kan: kanamycin, X-gal: 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactopyranoside, aph: kanamycin resistance gene, bla: ampicillin resistance gene; US: upstream, DS: downstream, WT: wild-type, SCO: single cross over, DCO: double cross over.