Figure 3.
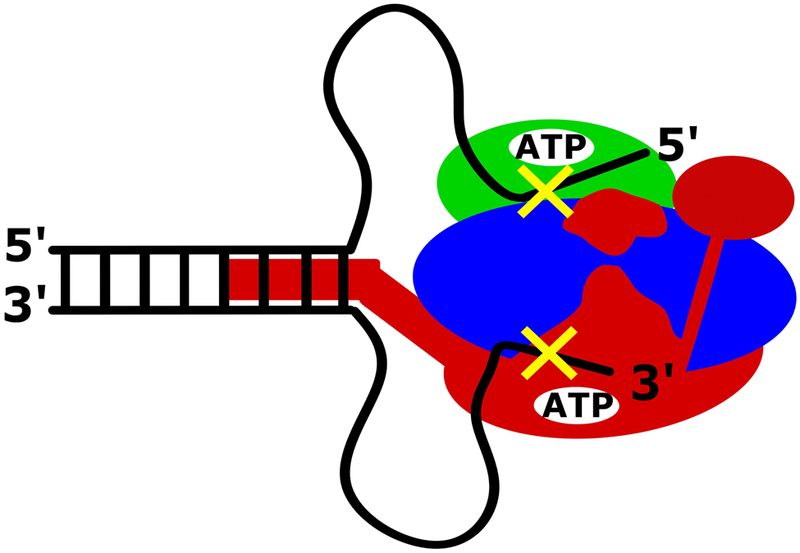
RecBCD can unwind DNA processively in the absence of ssDNA translocation by the canonical RecB and RecD motors. RecBCD can transiently unwind duplex DNA beyond the reverse polarity switches in the DNA backbone (indicated here by yellow x’s), which prevent the canonical RecB and RecD motors from translocating along the ssDNA. This activity is dependent upon the secondary translocase activity of RecBC that is fueled by the RecB ATPase activity and requires both the RecB arm domain and the RecB nuclease domain, but not nuclease activity. It is possible that the RecB arm act as a dsDNA translocase, pulling the dsDNA towards RecBCD, resulting in the formation of ssDNA loops.
