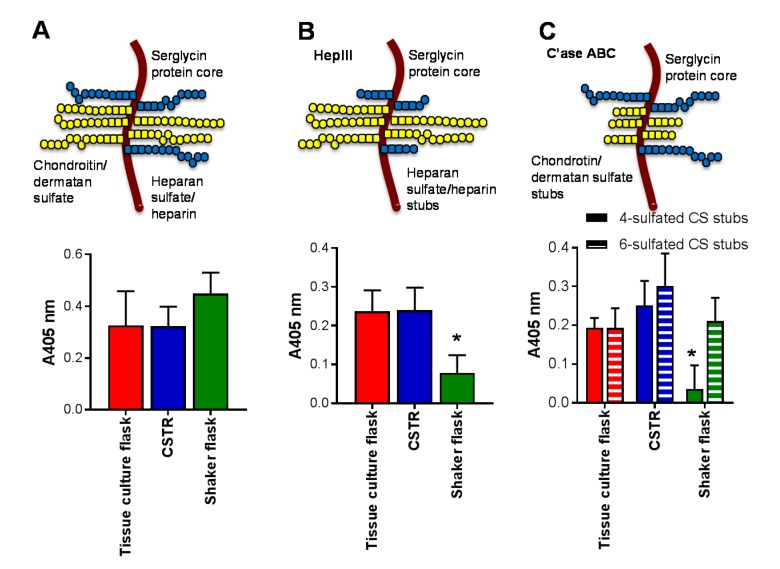
Figure 4.
The effect of bioreactors on the production of serglycin, heparin/heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. The schematic indicates the structure of serglycin with eight glycosaminoglycan attachment sites that can be decorated with either chondroitin/dermatan sulfate or heparin/heparan sulfate chains. The effect of glycosaminoglycan lyase digestion on the glycosaminoglycan chains are indicated in panels (B,C) with HepIII removing heparin/heparan sulfate chains to reveal a single stub structure and chondroitinase ABC (C’ase ABC) removing chondroitin/dermatan sulfate chains to reveal a stub structure. ELISA for the presence of (A) serglycin core protein; (B) heparin/heparan sulfate stubs detected using anti-heparan sulfate/heparin-stub antibody clone 3G10 following HepIII digestion, and (C) chondroitin sulfate stubs detected using anti-4-sulfated chondroitin sulfate stub antibody clone 2B6 and anti-6-sulfated chondroitin sulfate stub antibody clone 3B3 following C’ase ABC digestion. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation (n = 3). * indicates significant differences (p < 0.05) compared to tissue culture flasks analyzed by one-way ANOVA.