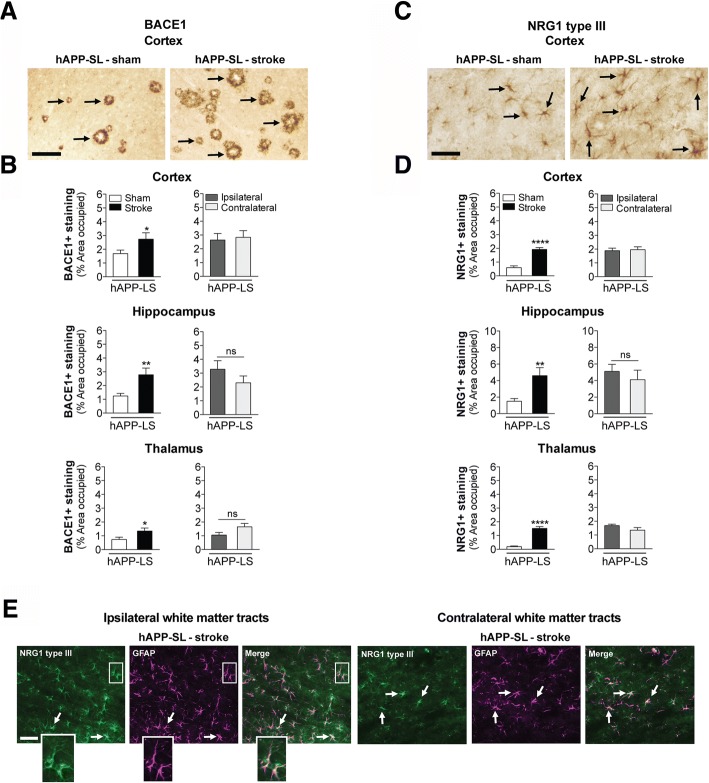
Fig. 8.
Stroke increases β-secretase (BACE) 1 and neuregulin (NRG) 1 type III immunostaining in aged hAPP-SL mice. a Representative 10× images of BACE1+ immunostaining (arrows) in the primary somatosensory cortex of 18 mo sham- or stroke-operated hAPP-SL mice. Scale bar, 125 μm. b Quantification revealed that relative to sham-operated hAPP-SL mice, the area occupied by BACE1+ staining was significantly higher in the cortex (top graph), hippocampus (middle graph), and thalamus (bottom graph) of the stroked hAPP-SL mice; no significant difference in the amount of BACE1+ staining was found between the ipsilateral versus contralateral hemisphere. c Representative 20× images of NRG1 type III+ immunostaining (arrows) in the primary somatosensory cortex of 18 mo sham- or stroke-operated hAPP-SL mice. Scale bar, 125 μm. d Quantification revealed that relative to sham-operated hAPP-SL mice, the area occupied by NRG1 type III+ staining was significantly higher in the cortex (top graph), hippocampus (middle graph), and thalamus (bottom graph) of the stroked hAPP-SL mice; no significant difference in the amount of NRG1 type III+ staining was found between the ipsilateral versus contralateral hemisphere. Data represent mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ****p<0.0001. e Representative 40× fluorescence images (n=3 mice/experimental group) from the 18 mo stroked hAPP-SL mouse sections showing NRG1 type III staining (green) within cells staining for the astrocytic marker, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, magenta), in the ipsilateral and contralateral white matter tracts (thalamus-internal capsule). Magnified outsets show GFAP+ astrocytes colocalized with NRG1 type III. Scale bar, 50 μm